Basophil-derived exosomes exacerbate systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating B-cell proliferation via miR-24550
- PMID: 40846943
- PMCID: PMC12374475
- DOI: 10.1186/s12916-025-04324-3
Basophil-derived exosomes exacerbate systemic lupus erythematosus by regulating B-cell proliferation via miR-24550
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a complex autoimmune disease where B-cell proliferation and activation play a pivotal role in pathogenesis. While the role of basophils in SLE is recognized, the impact of basophil-derived exosomes on B-cell proliferation and activation has not been thoroughly investigated.
Methods: Exosomes from human basophils in both resting and activated states were isolated and characterized. These exosomes were then co-cultured with B cells to assess their effects on B-cell survival and proliferation. To investigate the in vivo roles, a Pristane-induced lupus model in Mcpt8flox/flox CAGGCre-ERTM mice was utilized. The Pristane-Mcpt8flox/flox, CAGGCre-ERTM mice were analyzed for basophil-derived exosome accumulation in the spleen and kidneys, and the effects on immune cell proliferation and plasma cell-plasmablast balance were assessed. Transcriptomic analysis was conducted on basophil-derived exosomes to identify key non-coding RNAs. Lupus mice were humanized by transplanting peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with SLE into immunodeficient mice to evaluate the effects of intervening miR-24550 in B cells.
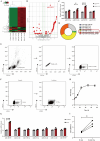
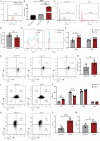
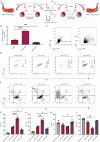
Results: Activated basophil-derived exosomes were found to enhance B-cell survival and proliferation in patients with SLE. In the lupus mouse model, basophil-derived exosomes accumulated primarily in the spleen and kidneys, inducing excessive immune cell proliferation and disrupting the plasma cell-plasmablast balance, which worsened kidney damage. Transcriptomic analysis revealed key non-coding RNAs within basophil-derived exosomes. Activated basophil-derived exosomes were internalized by B cells, releasing miR-24550, which promoted B-cell proliferation. In humanized SLE mice, inhibiting miR-24550 in B cells reduced immune hyperactivation and improved renal function, similar to the effects of inhibiting basophil-derived exosomes release in Pristane-Mcpt8flox/flox, CAGGCre-ERTM mice. Ultimately, basophil-derived exosomal miR-24550 promotes B-cell proliferation and activation by targeting Krüppel-like factor 5 (KLF5), which exacerbates SLE progression.
Conclusions: Basophil-derived exosomal miR-24550 promotes B-cell proliferation and activation by targeting KLF5, thereby exacerbating SLE progression. This study presents a novel strategy for SLE prevention and treatment.
Keywords: B cells; Basophils; Exosomes; Systemic lupus erythematosus; miR-24550.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Based on the modified SLE classification criteria formulated by the American College of Rheumatology in 1997, 48 patients with SLE were enrolled in this study at the Department of Nephrology between September 2020 and November 2024. This study was approved by the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University’s ethics committee (Approval no. YJYS2020107). Written informed consent was obtained from all the patients. Mcpt8flox/flox, CAGGCre−ERTM, Mcpt8flox/flox, and NKG mice were obtained from Cyagen Biosciences (License No. SCXK (Yue) 2020–0055). The maintenance of these mice was approved by the Ethics Committee for Experimental Animals of the Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University (Approval no. GDY2002081). All experiments were conducted under the national animal welfare guidelines. Consent for publication: All authors read and approved the manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Müller F, Taubmann J, Bucci L, Wilhelm A, Bergmann C, Völkl S, Aigner M, Rothe T, Minopoulou I, Tur C, et al. CD19 CAR t-cell therapy in autoimmune disease-a case series with follow-up. N Engl J Med. 2024;390(8):687–700. - PubMed
-
- Iype J, Odermatt A, Bachmann S, Coeudevez M, Fux M. IL-1β promotes immunoregulatory responses in human blood basophils. Allergy. 2021;76(7):2017–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

