Spatial transcriptomics elucidates localized immune responses in atherosclerotic coronary artery
- PMID: 40847214
- PMCID: PMC12514278
- DOI: 10.1038/s44321-025-00280-w
Spatial transcriptomics elucidates localized immune responses in atherosclerotic coronary artery
Abstract
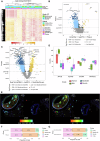
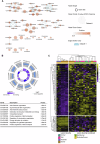
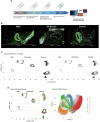
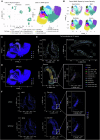
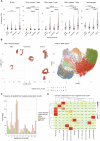
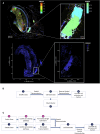
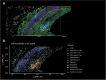
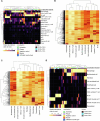
Atherosclerosis is characterized by the accumulation of lipids and immune cells in the arterial wall, leading to the narrowing and stiffening of blood vessels. Innate and adaptive immunity are involved in the pathogenesis of human atherosclerosis. However, spatial organization and roles of immune cells during disease progression remain poorly understood. A better understanding of the immune response's contribution to atherosclerosis progression could unveil novel therapeutic targets to mitigate plaque development and rupture, ultimately reducing cardiovascular events burden. Here, we utilised GeoMx® and CosMx™ technologies to analyse serial sections of human coronary arteries from patients with varying degrees of atherosclerotic lesion severity. Our work comprises a series of investigations and integrates findings from both datasets, including pathway analyses, cell typing, and neighbourhood analysis. This workflow highlights the power of combining these spatial transcriptomics platforms to elucidate biological processes at the single-cell level. Our approach unbiasedly identifies molecules and pathways of relevance to support the understanding of atherosclerosis pathogenesis and assess the potential for novel therapies.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; CosMx; GeoMx; Immune Cells; Spatial Omics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure and competing interests statement. The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Basatemur GL, Jørgensen HF, Clarke MCH, Bennett MR, Mallat Z (2019) Vascular smooth muscle cells in atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Cardiol 16:727–744 - PubMed
-
- Bleckwehl T, Babler A, Tebens M, Maryam S, Nyberg M, Bosteen M, Halder M, Shaw I, Fleig S, Pyke C et al (2025) Encompassing view of spatial and single-cell RNA sequencing renews the role of the microvasculature in human atherosclerosis. Nat Cardiovasc Res 4:26–44 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

