Identification and green synthesis of potato dry rot Fusarium falciforme silver nanoparticles, characterization and antibacterial activity
- PMID: 40847275
- PMCID: PMC12374413
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-025-07124-2
Identification and green synthesis of potato dry rot Fusarium falciforme silver nanoparticles, characterization and antibacterial activity
Abstract
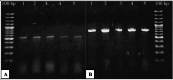
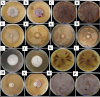
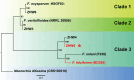
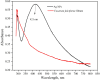
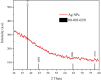
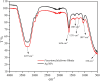
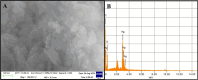
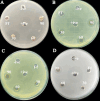
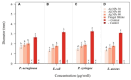
Potato tubers collected from different areas showed the prevalence of dry rot with characteristic white mycelia like symptoms of Fusarium pathogen. Fusarium species from diseased tubers were isolated based on morphological features. 18 S-Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) and Translation Elongation factor 1-α (TEF1-α) based analysis followed by phylogenetic tree constructed using ITS, TEF1-α and RNA polymerase II subunit B (RPB2) identified Fusarium isolates as Fusarium verticilloides, Fusarium soloni, Fusarium falciforme and Fusarium oxysporum. According to our knowledge, this study is the first report of the occurrence of Fusarium falciforme causing dry rot on potato tubers in Pakistan. The pathogenicity test confirmed the re-appearance of dry rot symptoms with Fusarium falciforme on potato tuber. The formation of Fusarium falciforme Ag NPs was confirmed using UV-Visible spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) analysis. The synthesized Ag NPs showed color change with Fusarium falciforme and accordingly, UV peak was observed at 431 nm. The XRD revealed Ag based specific angles at 36.14°, 44.26°, 64.42° and 77.44° corresponding to face cubic structure. Similarly, FTIR band absorption at 3297 cm-1, 1626 cm-1 and 1057 cm-1 ascribed the presence of various biomolecules with O-H, N-H and C-N stretching vibrations based on Ag NPs synthesis. SEM indicated 29 nm synthesized mainly spherical Ag NPs and EDS analysis showed the presence of Ag in NPs. Maximum zone of inhibition with Fusarium falciforme Ag NPs was observed against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas syringae and Staphylococcus aureus at 0.05 LSD significance.
Keywords: Fusarium falciforme; Antibacterial; Potato; Silver nanoparticles.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All authors have read and approved the manuscript. The tuber samples used in study were obtained with the permission of landowners at KP Pakistan and are used for research purpose only.
Figures



Similar articles
-
First identification of potato tuber rot caused by Penicillium solitum, its silver nanoparticles synthesis, characterization and use against harmful pathogens.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Oct 19;14:1255480. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1255480. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37929179 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of green Fe2O3 nanoparticles in controlling Fusarium fruit rot disease of loquat in Pakistan.Braz J Microbiol. 2023 Sep;54(3):1341-1350. doi: 10.1007/s42770-023-01050-x. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Braz J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37400611 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles from Asplenium dalhousiae and their potential biological properties.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 30;20(6):e0325533. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325533. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40587502 Free PMC article.
-
Recent insights into potato dry rot an emerging Disease: Focusing on pathogen diversity, host-pathogen interactions, and management strategies.Microb Pathog. 2025 Oct;207:107866. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2025.107866. Epub 2025 Jul 9. Microb Pathog. 2025. PMID: 40645351 Review.
-
Phytogenic nanoparticles: synthesis, characterization, and their roles in physiology and biochemistry of plants.Biometals. 2024 Feb;37(1):23-70. doi: 10.1007/s10534-023-00542-5. Epub 2023 Nov 2. Biometals. 2024. PMID: 37914858 Review.
References
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT Statistical Database. [Rome]; 2023: FAO.
-
- Azil N, Stefańczyk E, Sobkowiak S, Chihat S, Boureghda H, Sliwka S. Identification and pathogenicity of F. spp. associated with tuber dry rot and wilt of potato in Algeria. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2021;159:495–509. 10.1007/s10658-020-02177-5.
-
- Harish J, Jambhulkar PP, Bajpai R, Arya M, Babele PK, Chaturvedi SK, Kumar A, Lakshman DK. Morphological characterization, pathogenicity screening, and molecular identification of Fusarium spp. isolates causing post-flowering stalk rot in maize. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1121781. 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1121781. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

