Delayed Repolarization Caused by hERG Block With Different Drug Modalities Can Be Detected in Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes: Incubation Time Matters
- PMID: 40848285
- PMCID: PMC12374734
- DOI: 10.1111/cts.70283
Delayed Repolarization Caused by hERG Block With Different Drug Modalities Can Be Detected in Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes: Incubation Time Matters
Abstract
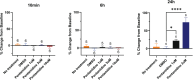
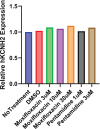
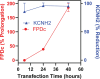
The intrinsic characteristics of oligonucleotides pose a challenge for their assessment in conventional primary in vitro cardiac models, which were designed for the acute application of small molecule agents and are not suitable for transfection and extended culture periods. Conversely, human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes (hiPSC-CM) offer a viable platform for the evaluation of agents over prolonged application and recording times. Our previous experiments demonstrated that a chronic protocol of 48 h is necessary to discern the functional effects of a siRNA targeting hERG in a stable cell line heterologously expressing hERG. To investigate whether a targeted hERG siRNA induces delayed repolarization in hiPSC-CM, we recorded field potentials (FPs) using a multielectrode array. FP duration (FPD) prolongation was noted as early as 10 min after exposure to moxifloxacin, whereas pentamidine required 24 h to induce FPD prolongation. Transfection with hERG-targeting siRNA reduced mRNA expression at 6 h post-transfection. However, FPD prolongation was only observed after 24 h post-transfection, with significantly larger effects at 48 h, which is indicative of the time needed for turnover of the hERG protein on the plasma membrane. Our findings provide compelling evidence that MEA recordings in hiPSC-CM can accurately detect disruptions in cardiac repolarization due to various mechanisms that impair hERG channel function, including direct channel blockade, inhibition of protein trafficking, and gene silencing via siRNA. The findings also indicate that indirect mechanisms of hERG knockdown, including gene silencing, require assessment at least 48 h following treatment to detect delayed repolarization in the hiPSC-CM model.
Keywords: PCR; hERG; hiPSC‐CM; multielectrode array; oligonucleotide; siRNA.
© 2025 The Author(s). Clinical and Translational Science published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Amgen Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Disruption of protein quality control of the human ether-à-go-go related gene K+ channel results in profound long QT syndrome.Heart Rhythm. 2022 Feb;19(2):281-292. doi: 10.1016/j.hrthm.2021.10.005. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Heart Rhythm. 2022. PMID: 34634443 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Multi-laboratory comparisons of manual patch clamp hERG data generated using standardized protocols and following ICH S7B Q&A 2.1 best practices.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 16;15(1):29995. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-15761-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40819150 Free PMC article.
-
Opioids-induced inhibition of HERG ion channels and sudden cardiac death, a systematic review of current literature.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jul;34(5):279-285. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2023.03.006. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 37015297
-
Management of urinary stones by experts in stone disease (ESD 2025).Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025 Jun 30;97(2):14085. doi: 10.4081/aiua.2025.14085. Epub 2025 Jun 30. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2025. PMID: 40583613 Review.
References
-
- Fire A., Xu S., Montgomery M., Kostas S. A., Driver S. E., and Mello C. C., “Potent and Specific Genetic Interference by Double‐Stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans ,” Nature 391 (1998): 806–811. - PubMed
-
- Qu Y., Henderson K. A., T. A. Harper, Jr. , and Vargas H. M., “Scientific Review of the Proarrhythmic Risks of Oligonucleotide Therapeutics: Are Dedicated ICH S7B/E14 Studies Needed for Low‐Risk Modalities?,” Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 116 (2024): 96–105. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

