Third exposure to COVID-19 infection or vaccination differentially impacts T cell responses
- PMID: 40848990
- PMCID: PMC7618389
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jinf.2025.106598
Third exposure to COVID-19 infection or vaccination differentially impacts T cell responses
Abstract
Background: In 2021, the rapid rollout of two doses of SARS-CoV-2 vaccines reduced COVID-19 severity and mortality. However, further vaccine doses as a prime-boost schedule were limited, and lifting of public health restrictions by late 2021 frequently led to infection, rather than vaccine, as a third exposure.
Objective: To compare how the third exposure through mRNA booster or SARS-CoV-2 infection shapes humoral and cellular immunity following two vaccine doses.
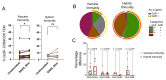
Methods: We compared immune responses after the third exposure in healthy adults enrolled in the UCLH-Crick Legacy cohort study (NCT04750356) between those receiving ancestral spike-encoded mRNA booster (vaccine immunity, n = 38) or COVID-19 infection (hybrid immunity, n = 13) following two vaccine doses. Immune profiles were evaluated using live virus neutralization assays, IFN-γ ELISpot, Luminex assay, flow cytometry and mass cytometry.
Results: Both total anti-Spike IgG and variant-specific neutralising antibodies were comparable following infection or vaccine as a third exposure. Overall, T cell populations were similar but functionally different. CD8⁺ Effector Memory (TEM) cells in the vaccine group showed higher expression of CD69 and Granzyme B following stimulation with SARS-CoV-2 Spike peptides. In contrast, the hybrid group produced higher levels of innate immune associated cytokines IL-10 and IL-34, as well as the T cell homing chemokine CCL25, after stimulation.
Conclusions: While both exposures generated comparable breadth of protection against SARS-CoV-2 variants, our findings suggest that the route of third exposure influences different aspects of the immune response, warranting further investigation into long-term immunity at both systemic and mucosal sites.
Keywords: Immunity; Infection exposure; SARS-CoV-2; T cells; Vaccination.
Crown Copyright © 2025. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: CSw reports interests unrelated to this Correspondence: grants from BMS, Ono- Pharmaceuticals, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Roche-Ventana, Pfizer and Archer Dx, unrelated to this Correspondence; personal fees from Genentech, Sarah Canon Research Institute, Medicxi, Bicycle Therapeutics, GRAIL, Amgen, AstraZeneca, BMS, Illumina, GlaxoSmithKline, MSD, and Roche-Ventana, unrelated to this Correspondence; and stock options from Apogen Biotech, Epic Biosciences, GRAIL, and Achilles Therapeutics, unrelated to this Correspondence. DLVB reports discussions between the Crick and GSK for commercial antiviral testing, and grants to the Crick from AstraZeneca unrelated to this Correspondence. EW reports consulting for AstraZeneca and CSL-Seqirus unrelated to this article. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Office NA. The rollout of the COVID-19 vaccination programme in England. National Audit Office; 2022.
-
- Graham C, Lechmere T, Rehman A, Seow J, Kurshan A, Huettner I, et al. The effect of Omicron breakthrough infection and extended BNT162b2 booster dosing on neutralization breadth against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern. PLoS Pathog. 2022;18(10):e1010882. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010882. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

