Modulation of neuroimmune cytokine networks by antidepressants: implications in mood regulation
- PMID: 40849324
- PMCID: PMC12375052
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03532-y
Modulation of neuroimmune cytokine networks by antidepressants: implications in mood regulation
Abstract
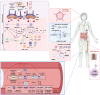
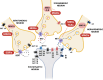
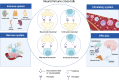
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is increasingly recognized as a neuroinflammatory condition characterized by dysregulated cytokine networks. This comprehensive review examines the immunomodulatory effects of antidepressant medications, revealing their significant impact on Th1/Th2 cytokine balance beyond their classical neurotransmitter actions. Clinical data show that diverse antidepressant classes consistently demonstrate immunomodulatory properties that extend beyond their classical neurotransmitter effects. These medications reduce pro-inflammatory markers (IFN-γ, TNF-α, IL-6) while enhancing anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10, TGF-β), effects particularly relevant for treatment-resistant cases with elevated baseline inflammation. The therapeutic potential of these immunoregulatory effects is supported by emerging interventions, including low-dose IL-2 immunotherapy, vagus nerve stimulation, and microbiota-targeted therapies, which show promise for specific depression subtypes. Importantly, these approaches appear most effective when guided by inflammatory biomarkers, suggesting a path toward personalized treatment strategies. By integrating findings from clinical studies and translational research, this work establishes immune modulation as a fundamental component of antidepressant action. The review provides a framework for developing next-generation treatments that target neuroimmune pathways in MDD, with particular emphasis on practical applications for treatment-resistant cases. These insights bridge the gap between neuropharmacology and clinical psychiatry, offering new therapeutic possibilities for patients with inflammation-associated depression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New generation antidepressants for depression in children and adolescents: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 May 24;5(5):CD013674. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013674.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34029378 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant Effect of Ketamine on Inflammation-Mediated Cytokine Dysregulation in Adults with Treatment-Resistant Depression: Rapid Systematic Review.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Sep 16;2022:1061274. doi: 10.1155/2022/1061274. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36160713 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatments in panic disorder in adults: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 28;11(11):CD012729. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012729.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38014714 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Spijker J, Graaf R, Bijl RV, Beekman ATF, Ormel J, Nolen WA. Functional disability and depression in the general population. Results from the Netherlands mental health survey and incidence study (NEMESIS). Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2004;110:208–14. - PubMed
-
- Becker AE, Kleinman A. Mental health and the global agenda. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:66–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

