Large-scale GWAS of strabismus identifies risk loci and provides support for a link with maternal smoking
- PMID: 40849414
- PMCID: PMC12375114
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-62456-9
Large-scale GWAS of strabismus identifies risk loci and provides support for a link with maternal smoking
Abstract
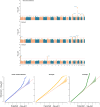
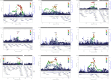
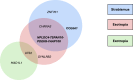
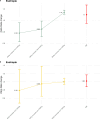
Strabismus is a common pediatric eye misalignment and has complex genetic and environmental causes. Previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS) encountered difficulties in identifying strabismus risk variants due to heterogeneity and small samples. We performed large meta-analyses of 11 European-ancestry GWAS (7 sources), analysing broad strabismus (20,464 cases, 954,921 controls) and subtypes (esotropia/exotropia). We discovered 4 loci (e.g., NPLOC4-TSPAN10-PDE6G-FAAP100, COL6A1) for strabismus and 5 additional loci (e.g., CHRNA4, MAD1L1) for strabismus subtypes and we successfully replicated the previously reported strabismus variant near NPLOC4-TSPAN10-PDE6G-FAAP100. Using mendelian randomisation, we found genetic evidence supporting maternal smoking as a causal risk factor for strabismus in offspring.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Donahue, S. P. Pediatric Strabismus. N. Engl. J. Med.356, 1040–1047 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Hashemi, H. et al. Global and regional prevalence of strabismus: a comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis. Strabismus27, 54–65 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Harrad, R. & Williams, C. Risk, causes and outcomes of visual impairment after loss of vision in the non-amblyopic eye, a population-based study. Surv. Ophthalmol.48, 235–236 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Yang, Y. et al. Maternal smoking during pregnancy and the risk of strabismus in offspring: a meta-analysis. Acta Ophthalmol.97, 353–363 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

