Brain-region-specific lipid dysregulation in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in a primate model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40849420
- PMCID: PMC12374971
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-025-01109-6
Brain-region-specific lipid dysregulation in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in a primate model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
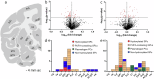
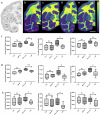
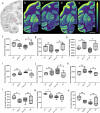
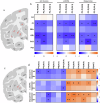
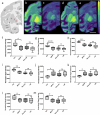
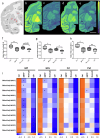
L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia (LID) is a significant and treatment-limiting complication in Parkinson's disease (PD) therapy, yet its mechanisms remain poorly understood. We used high-resolution mass spectrometry imaging to map brain-region-specific alterations of glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids in a female macaque model of PD with and without LID following chronic L-DOPA treatment. LID was associated with depletion of antioxidant plasmalogen phosphatidylcholines in the globus pallidus interna, claustrum, and precentral gyrus-regions critical for motor function-and elevations of polyunsaturated fatty acid-containing glycerophospholipids, indicative of increased membrane fluidity. This lipid profile differed from similarly treated non-dyskinetic animals, suggesting lipid composition mediates differential susceptibility to LID. Lipid alterations correlated strongly with dyskinesia severity, dopamine, and L-DOPA concentrations, supporting a mechanistic link between lipid metabolism, neurotransmitter dysregulation, and LID. This comprehensive spatial lipidomic analysis identifies region-specific lipid dysregulation as a novel aspect of LID pathology, highlighting lipid pathways as potential therapeutic targets for mitigating dyskinesia.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Poewe, W. et al. Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim.3, 1–21 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Huot, P., Johnston, T. H., Koprich, J. B., Fox, S. H. & Brotchie, J. M. The pharmacology of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson’s disease. Pharm. Rev.65, 171–222 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Jenner, P. Molecular mechanisms of L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.9, 665–677 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Wenk, M. R. The emerging field of lipidomics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov.4, 594–610 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Han, X. Lipidomics for studying metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol.12, 668–679 (2016). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

