Lp‑PLA2 in the cancer landscape: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic potential (Review)
- PMID: 40849801
- PMCID: PMC12425350
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2025.5793
Lp‑PLA2 in the cancer landscape: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic potential (Review)
Abstract
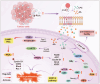
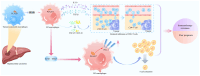
Lipoprotein‑associated phospholipase A2 (Lp‑PLA2), an important member of the phospholipase A2 superfamily, was originally investigated for its proinflammatory role in cardiovascular diseases. Recent studies have revealed its significant role in tumorigenesis: It can act as either a tumor promoter or a tumor suppressor depending on the context. The present review systematically outlined the dual mechanisms by which Lp‑PLA2 contributes to cancer pathogenesis. As a tumor promoter, it promotes cancer progression via the induction of epithelial‑mesenchymal transition, glutathione peroxidase 4‑mediated resistance to ferroptosis, and vascular endothelial growth factor‑-dependent angiogenesis; conversely, as a tumor suppressor, it inhibits tumor growth by suppressing the Wnt/β‑catenin pathway in breast cancer gene 1‑mutated cancers or by promoting apoptosis. Mechanistic investigations clarify the interactions between Lp‑PLA2 and critical oncogenic pathways, such as the Notch and HIF1α pathways, while emphasizing the functional dichotomy that is influenced by the microenvironment. Current evidence supports the development of microenvironment‑guided targeting strategies and the potential value of Lp‑PLA2 as a prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target. These findings contribute to a theoretical framework for comprehending the context‑dependent roles of Lp‑PLA2 and may guide the development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: biomarker; cancer; ferroptosis; lipoprotein‑associated phospholipase a2; molecular mechanism; therapeutic target; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

