Reg3β promotes chondrocyte proliferation and ECM metabolism during acetabular roof remodeling in a rat model of DDH‑induced residual dysplasia
- PMID: 40849812
- PMCID: PMC12382431
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13653
Reg3β promotes chondrocyte proliferation and ECM metabolism during acetabular roof remodeling in a rat model of DDH‑induced residual dysplasia
Abstract
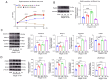
Residual acetabular dysplasia (RAD) is a common complication after the successful management of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH). RAD remodeling is important for predicting the outcome of the affected hip, and optimal treatment can be chosen accordingly. Regenerating islet‑derived protein 3‑β (Reg3β), a multifaceted cytokine, is a prognostic marker for inflammation and cardiac disease. Nevertheless, the roles of Reg3β in RAD remain unclear. Consequently, the aim of the present study was to assess the role of Reg3β in RAD and explore its related functions in chondrocytes in vitro. First, remodeling of the affected hip after fixation removal was observed in a neonatal rat DDH model, which simulated the process of RAD. Reg3β expression in RAD was upregulated at weeks 1, 2 and 4, as determined by western blot analysis. The serum concentration of Reg3β was greater than that of normal rats at 2 weeks and returned to normal levels at 4 weeks. Subsequently, it was found that Reg3β promoted cell proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) metabolism via the Jak2/Stat3/Socs3 signaling pathway through gene knockdown and addition of recombinant Reg3β protein. These findings suggest that Reg3β is a novel potent prognostic biomarker for the remodeling of RAD via regulation of chondrocyte proliferation and metabolism of the ECM.
Keywords: anti‑apoptosis; chondrocytes; extracellular matrix metabolism; proliferation; regenerating islet‑derived protein 3β; residual dysplasia of the hip.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


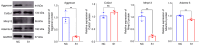

Similar articles
-
Splinting for the non-operative management of developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) in children under six months of age.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Oct 10;10(10):CD012717. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012717.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36214650 Free PMC article.
-
What Are the Sex-Based Differences of Acetabular Coverage Features in Hip Dysplasia?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Nov 1;482(11):1971-1983. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003126. Epub 2024 Jul 12. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38996383
-
Is Prior Nonoperative or Operative Treatment of Dysplasia of the Hip Associated With Poorer Results of Periacetabular Osteotomy?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024 Nov 1;482(11):1987-1996. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003150. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2024. PMID: 38917051
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kiani SN, Gornitzky AL, Matheney TH, Schaeffer EK, Mulpuri K, Shah HH, Yihua G, Upasani V, Aroojis A, Krishnamoorthy V, et al. A prospective, multicenter study of developmental dysplasia of the hip: What can patients expect after open reduction? J Pediatr Orthop. 2023;43:279–285. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002383. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

