Resistance Training Beyond Momentary Failure: The Effects of Past-Failure Partials Versus Initial Partials on Calf Muscle Hypertrophy Among a Resistance-Trained Cohort
- PMID: 40850937
- PMCID: PMC12375417
- DOI: 10.1002/ejsc.70030
Resistance Training Beyond Momentary Failure: The Effects of Past-Failure Partials Versus Initial Partials on Calf Muscle Hypertrophy Among a Resistance-Trained Cohort
Abstract
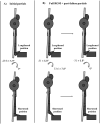
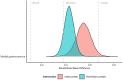
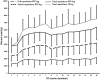
This study compared calf training with initial partial repetitions versus full range-of-motion (ROM) repetitions followed by past-failure partials on gastrocnemius hypertrophy. Twenty-three participants (men: n = 16 and women: n = 7) performed four sets of unilateral Smith machine calf raises to momentary failure twice a week for 8 weeks. One leg was trained using initial partials to their individualized maximum dorsiflexion ROM. The contralateral leg was trained with a full ROM and continued with past-failure partials after failure in peak plantarflexion. Medial gastrocnemius muscle thickness was measured with ultrasonography both baseline and postintervention. A Bayesian framework was used to estimate the average treatment effect (ATE) using credible intervals and Bayes factors (BFs). The ATE posterior distribution indicated a greater increase in muscle hypertrophy for the initial partial condition (0.40 [95% CrI: -0.06 to 0.85 mm]; p (> 0) = 0.958), with a BF of 1.2 suggesting "anecdotal" evidence in favor of an effect. Within-condition analyses using standardized mean difference estimates indicated that the interventions were likely to produce medium to large improvements. These findings suggest that both initial partials and past-failure partials are viable strategies for achieving gastrocnemius hypertrophy. Although the average change favored initial partials, the estimated difference was uncertain, and the Bayes factor provided only anecdotal support for a differential effect.
Keywords: calves; muscle length; muscle thickness; plantarflexion; ultrasonography.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Sport Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH on behalf of European College of Sport Science.
Conflict of interest statement
B.J.S. formerly served on the scientific advisory board for Tonal Corporation, a manufacturer of fitness equipment. No other authors report any declaration of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Aczel, B. , Palfi B., Szollosi A., et al. 2018. “Quantifying Support for the Null Hypothesis in Psychology: An Empirical Investigation.” Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science 1, no. 3: 357–366. 10.1177/2515245918773742. - DOI
-
- Burke, R. , Piñero A., Mohan A. E., et al. 2024. “Exercise Selection Differentially Influences Lower Body Regional Muscle Development.” Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise, 1–11.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

