Unlocking learning: evaluating case-based learning versus escape rooms for first-year dental students: a quasi-experimental study
- PMID: 40851943
- PMCID: PMC12369800
- DOI: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003444
Unlocking learning: evaluating case-based learning versus escape rooms for first-year dental students: a quasi-experimental study
Abstract
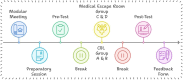
Background: This study evaluates the effectiveness of two small-group teaching methods - case-based learning (CBL) and escape room activities - on first-year dental students' performance and perception, focusing on the neuro-endocrine module. The escape room method incorporates gamification and includes tasks related to basic and relevant clinical sciences, such as trauma scenarios, cranium models, and virtual cadaveric dissections.
Objectives: The primary objective was to assess student performance using two different learning strategies. A secondary objective was to gauge students' perceptions of learning through these activities.
Methods: A quasi-experimental study involved 50 first-year dental students from a University located in Islamabad, Pakistan. Initially, the class was divided into two groups, and students received the learning objectives a day prior. They were randomly assigned into four groups 10 minutes before the activities: two groups proceeded with CBL and two engaged in the escape room. Both interventions required teamwork and collaboration while following the same objectives, which included tasks related to basic and relevant clinical sciences. Pre- and post-tests assessed performance, while perceptions were evaluated through a Likert scale feedback form based on Kirkpatrick's Model. Data were analyzed using SPSS 26 with appropriate statistical comparisons.
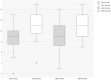
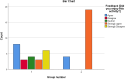
Results: Both groups showed significant score improvements (P < 0.001), but there were no significant differences between the two interventions (P = 0.855, P = 0.652). Chi-square tests indicated higher enjoyment and perceived usefulness for the Escape Room.
Conclusion: Both teaching methods effectively improved student performance. Incorporating gamification and interactive tasks has the potential to enhance teamwork and satisfaction.
Keywords: case-based learning (CBL); dental students; escape room; gamification; medical education; small group teaching.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The educational effects of portfolios on undergraduate student learning: a Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) systematic review. BEME Guide No. 11.Med Teach. 2009 Apr;31(4):282-98. doi: 10.1080/01421590902889897. Med Teach. 2009. PMID: 19404891
-
Development and Evaluation of a Case-Based Serious Game for Diagnosis and Treatment Planning in Orthodontic Education: Quasi-Experimental Study.JMIR Serious Games. 2025 Aug 27;13:e73956. doi: 10.2196/73956. JMIR Serious Games. 2025. PMID: 40864887 Free PMC article.
-
Traditional medical education under siege: the revolutionary integration of virtual reality and gamification in medical escape rooms.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Jul 1;25(1):898. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07367-5. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40598049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effectiveness of case-based learning in health professional education. A BEME systematic review: BEME Guide No. 23.Med Teach. 2012;34(6):e421-44. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.680939. Med Teach. 2012. PMID: 22578051
References
-
- Hopper MK. Alphabet soup of active learning: comparison of PBL, CBL, and TBL. HAPS Educ 2018;22:144–49.
-
- Michael J. Where’s the evidence that active learning works? Adv Physiol Educ 2006;30:159–67. - PubMed
-
- Raza SA, Qazi W, Umer B. Examining the impact of case-based learning on student engagement, learning motivation and learning performance among university students. J Appl Res High Educ 2019.
-
- Cain J. Exploratory implementation of a blended format escape room in a large enrollment pharmacy management class. Curr Pharm Teach Learn 2019;11:44–50. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Erratum in: Curr Pharm Teach Learn. 2021 Feb;13(2):189-191. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
