The effects of GLP-1 agonists on HbA1c and insulin dose among patients with type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 40852189
- PMCID: PMC12367517
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1550938
The effects of GLP-1 agonists on HbA1c and insulin dose among patients with type 1 diabetes
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) is a common chronic disease, and there is a rising trend globally; insulin is the mainstay therapy. Despite improvements in insulin delivery and monitoring, a significant percentage of patients still fail to reach glycemic targets. There is an increasing interest in using glucagon-like receptor agonists as adjuvant therapy. A high risk of bias limits meta-analysis on the effectiveness of GLP-1 agonists. This meta-analysis aimed to assess the effects of GLP-1 agonists on HbA1c and total daily insulin dose in T1DM. We searched PubMed, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar for articles investigating the effects of GLP-1 agonists on the HbA1c and total daily insulin dose without limitation to the publication date. The keywords used were GLP-1 agonists, liraglutide, albiglutide, exenatide, glycated hemoglobin, HbA1c, insulin dose, and glycemic control. Out of the 713 articles retrieved, 21 full texts were screened, and 10 trials were included in the meta-analysis. GLP-1 agonists are more effective than placebo in HbA1c reduction, Z = 5.27, SMD, 0.23, 95% confidence interval (CI), 0.14-0.32, with 1.2 mg and 1.8 mg more effective than 0.6 mg, SMD, -0.87, 95% CI, -1.60 to 0.13, and SMD, -0.79, 95% CI, -1.18 to 0.41, respectively. GLP-1 agonists reduce total daily insulin dose SMD, 2.21, 95% CI, 0.43-3.98 with no significant differences between different doses. GLP-1 agonists were effective in HbA1c and total daily insulin reduction among patients with T1DM. Liraglutide 1.2 mg may be more beneficial; further randomized trials focusing on different doses of GLP-1 agonists and hypoglycemia risk are recommended.
Keywords: HbA1c; glucagon-like peptide agonists; insulin dose; insulin reduction; type 1 diabetes.
Copyright © 2025 Alhowiti and Mirghani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

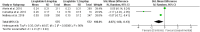
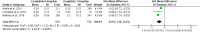
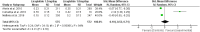


Similar articles
-
Dipeptidyl-peptidase (DPP)-4 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 analogues for prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its associated complications in people at increased risk for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 10;5(5):CD012204. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012204.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28489279 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin and glucose-lowering agents for treating people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Sep 24;9(9):CD011798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30246878 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and mixed-treatment comparison analysis.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017 Apr;19(4):524-536. doi: 10.1111/dom.12849. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017. PMID: 27981757
-
The quantity, quality and findings of network meta-analyses evaluating the effectiveness of GLP-1 RAs for weight loss: a scoping review.Health Technol Assess. 2025 Jun 25:1-73. doi: 10.3310/SKHT8119. Online ahead of print. Health Technol Assess. 2025. PMID: 40580049 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide analogues for type 2 diabetes mellitus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Oct 5;2011(10):CD006423. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006423.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011. PMID: 21975753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Szadkowska A, Michalak A, Chylińska-Frątczak A, Baranowska-Jaźwiecka A, Koptas M, Pietrzak I, et al. Achieving target levels for vascular risk parameters in Polish school-age children with type 1 diabetes - a single center study. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 31:1073–9. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2018-0098, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mirghani H, Alrasheed T, Kalantan M, Idris SM, Adawi G. Diabulimia, the associations, and management: A narrative review. Tekyo Med J. (2022) 45:4549–54556.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

