Emerging Plant-Based Nanotechnological Advances and Molecular Insights for Type‑2 Diabetes, Diagnosis and Treatments-Recent Trends and Future Prospects
- PMID: 40852224
- PMCID: PMC12368732
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01900
Emerging Plant-Based Nanotechnological Advances and Molecular Insights for Type‑2 Diabetes, Diagnosis and Treatments-Recent Trends and Future Prospects
Abstract
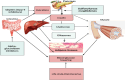
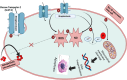
Type-2 diabetes, characterized by aberrant insulin secretion or increased hepatic glucose synthesis, accounts for approximately 90% of diabetes issues. This study explores current molecular and cellular advances related to T2D pathogenesis. Recent research on T2D about intracellular signaling cascades, inflammation, autophagy, genetics, and epigenetic changes is explained discretely. The present review discusses the available antidiabetic therapeutic strategies currently commercialized as well as their limitations that need to be acknowledged. Specifically, the review discusses how nanotechnology-based approaches nullify conventional antidiabetic therapeutics' inadequacy and heterogeneous nanoparticulate systems have been explored in diabetes research, and they're also listed in a tabular format. Furthermore, the research offers many strategic hypotheses as a potential application of nanotechnology in the future to improve the management of type-2 diabetes by developing a targeted nanodelivery system. In particular, attempts have been made to develop new treatment approaches based on nanotechnology that take advantage of autophagy and inflammasome target sites that have been previously identified. An explanation of how a smart targeted nano delivery system can inhibit the Wnt signaling pathway (inhibiting Gsk-3β), inhibit the inflammasome (inhibiting NLRP3), and activate autophagy target points (protecting the Atg3/Atg7 complex from oxidative stress) is provided through graphical description, which may mitigate the severity of type-2 diabetes.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type 1 Diabetes: A Guide to Autoimmune Mechanisms for Clinicians.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Aug;27 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):40-56. doi: 10.1111/dom.16460. Epub 2025 May 15. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40375390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular prospect of type-2 diabetes: Nanotechnology based diagnostics and therapeutic intervention.Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021 Jun;22(2):421-451. doi: 10.1007/s11154-020-09606-0. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2021. PMID: 33052523 Review.
-
The Lived Experience of Autistic Adults in Employment: A Systematic Search and Synthesis.Autism Adulthood. 2024 Dec 2;6(4):495-509. doi: 10.1089/aut.2022.0114. eCollection 2024 Dec. Autism Adulthood. 2024. PMID: 40018061 Review.
References
-
- Kalyani V. C., Kataria N., Kumari K.. Pattern of Diet Consumption and Levels of Knowledge Regarding Diabetes among Diabetic Adults Belongs to Rural and Urban Community Areas, Uttarakhand: A Cross-sectional Comparative Survey. J. Appl. Sci. Clin. Pract. 2025;6(1):21–26. doi: 10.4103/jascp.jascp_51_24. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
