Molecular Networking-Guided Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Isolariciresinol and Seco-Isolariciresinol Type Lignans from Alnus japonica
- PMID: 40852275
- PMCID: PMC12368658
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c05794
Molecular Networking-Guided Isolation of Anti-Inflammatory Isolariciresinol and Seco-Isolariciresinol Type Lignans from Alnus japonica
Abstract
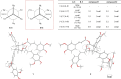
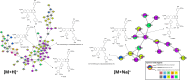
A comparative analysis of UPLC-DAD and MS chromatograms revealed distinct chemical profiles between the methanolic extracts of the branch and cortex of Alnus japonica. MS/MS-based molecular networking further identified unique molecular features present in the branch extract, which facilitated the targeted isolation of five previously undescribed lignan derivatives. The structures of these compounds were elucidated using 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy, along with high-resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS). The anti-inflammatory potential of the isolated compounds was evaluated by measuring the inhibition LPS-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells. Notably, compounds 1-5 exhibited significant NO inhibitory activity, with IC50 values of 3.7 and 7.4 μM.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures







References
-
- Tung N. H., Suzuki M., Uto T., Morinaga O., Kwofie K. D., Ammah N., Koram K. A., Aboagye F., Edoh D., Yamashita T., Yamaguchi Y., Setsu T., Yamaoka S., Ohta N., Shoyama Y.. Anti-trypanosomal activity of diarylheptanoids isolated from the bark of Alnus japonica . Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014;42:1245–1260. doi: 10.1142/S0192415X14500785. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
