Hepatoprotective Potential of Green Synthesized Nanoparticles from Citrus reticulata Peel Extract against HFS Diet-Induced NASH in Mice, Integrated with Chemical Profiling and Molecular Modeling
- PMID: 40852285
- PMCID: PMC12368685
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03992
Hepatoprotective Potential of Green Synthesized Nanoparticles from Citrus reticulata Peel Extract against HFS Diet-Induced NASH in Mice, Integrated with Chemical Profiling and Molecular Modeling
Abstract
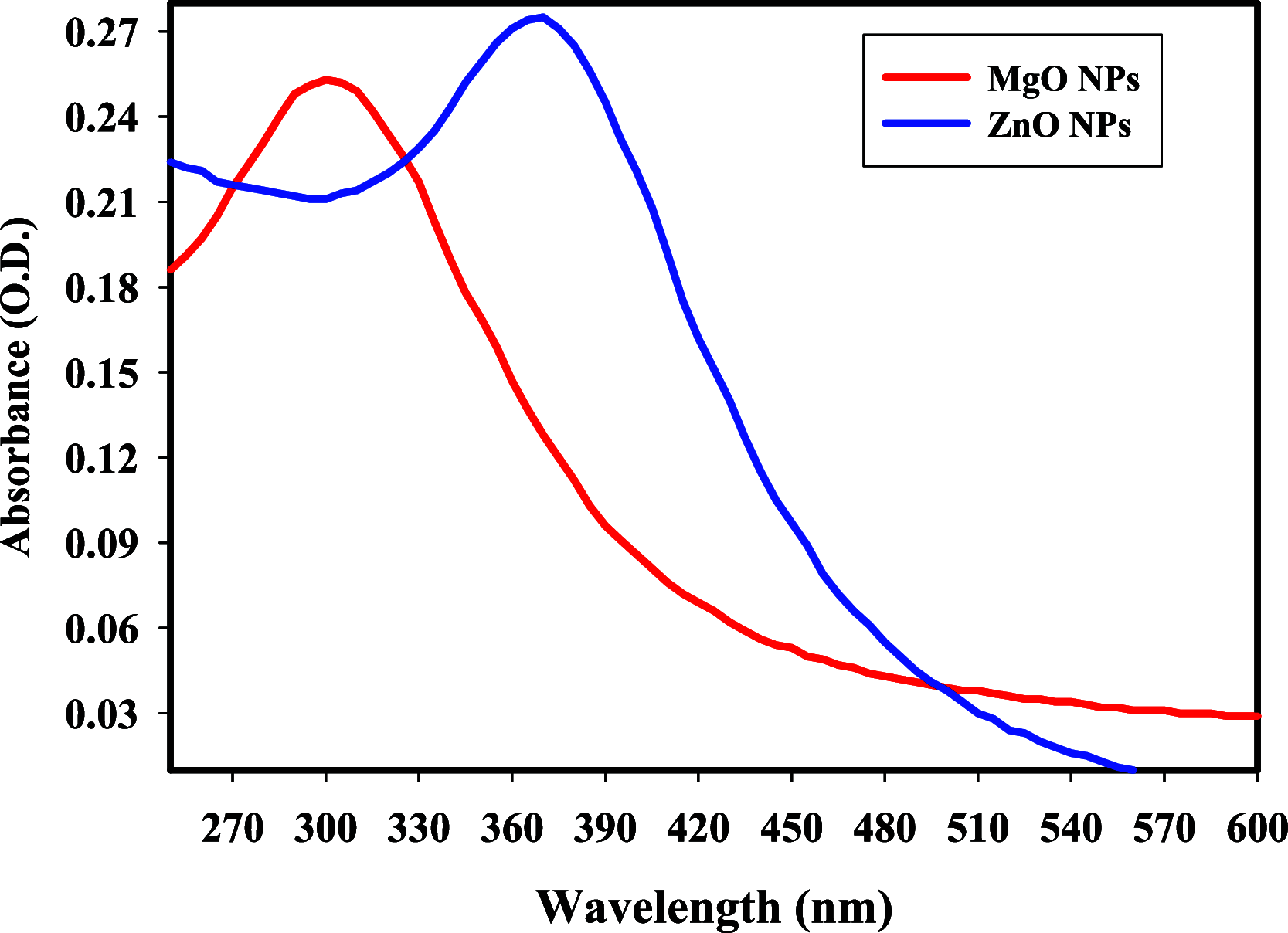
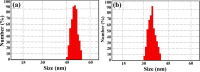
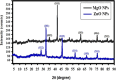
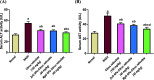
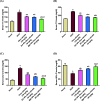
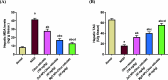
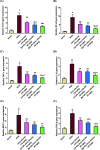
Citrus reticulata is known for its wide variety of secondary metabolites, including essential oil, alkaloids, flavonoids, and phenolic acids, which are considered the reason for its diverse potential medical uses. Herein, Citrus reticulata extract was prepared using different formulas of metal oxide nanoparticles as ZnO NPs and MgO NPs with 22.5 ± 1.3 and 18.3 ± 1.5 nm average particle sizes, respectively. The protective effects of Citrus reticulata extract and its two nano formulas against NASH induced by a high-fat, high-sucrose (HFS) diet in mice were evaluated. The NASH mice showed hepatic steatosis, inflammation, reduced liver function, increased body, liver, and fat weights, elevated hepatic index, and disrupted serum lipid profiles. Additionally, the mice displayed heightened hepatic oxidative stress and increased expression of inflammatory and profibrotic markers, along with altered lipid metabolism, indicated by elevated levels of SIRT-1, FGF-21, and SREBP-1c. Notably, treatment with Citrus reticulata extract and its metallic nanoparticle formulations alleviated these abnormalities, with the most significant improvement observed in the MgO NP formulation. Finally, Citrus reticulata extract was subjected to a deep phytochemical screening through Liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis, revealing the presence of a high diversity of polyphenolics that may contribute to the suggested therapeutic effects of the Citrus reticulata crude extract. A molecular docking study highlighted the binding affinities of all identified flavonoid compounds, especially Quercetin, toward IL-1β, TNF-α, and TGF-β target proteins. This shows good translation for the cumulative anti-inflammatory effect depicted by the Citrus reticulata crude extract. Thermodynamic stability of Quercetin toward each bound proinflammatory protein was confirmed through 150 ns all-atom molecular dynamics simulations. Overall, current findings suggest that Citrus reticulata exerts a protective effect against NASH, which could be enhanced by nano formulas.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures






References
-
- Prakash S., Rai U., Kosuru R., Tiwari V., Singh S.. Amelioration of diet-induced metabolic syndrome and fatty liver with sitagliptin via regulation of adipose tissue inflammation and hepatic Adiponectin/AMPK levels in mice. Biochimie. 2020;168:198–209. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2019.11.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Teng W., Zhao L., Yang S., Zhang C., Liu M., Luo J., Jin J., Zhang M., Bao C., Li D.. et al. The hepatic-targeted, resveratrol loaded nanoparticles for relief of high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Controlled Release. 2019;307:139–149. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.06.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang R., Chu K., Zhao N., Wu J., Ma L., Zhu C., Chen X., Wei G., Liao M.. Corilagin Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in High-Fat Diet-Induced C57BL/6 Mice by Ameliorating Oxidative Stress and Restoring Autophagic Flux. Front. Pharmacol. 2020;10:1693. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01693. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
