Targeting Cancer with New Morpholine-Benzimidazole-Oxadiazole Derivatives: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Computational Insights
- PMID: 40852298
- PMCID: PMC12368815
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c03795
Targeting Cancer with New Morpholine-Benzimidazole-Oxadiazole Derivatives: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, and Computational Insights
Abstract
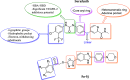
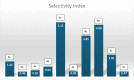
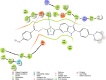
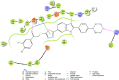
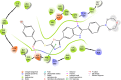
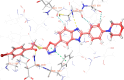
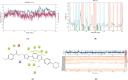
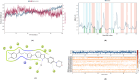
Cancer remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, characterized by uncontrolled cell proliferation, invasion of surrounding tissues, and metastasis to distant organs. Among various malignancies, colon cancer is particularly aggressive and often associated with poor prognosis in advanced stages. This study presents the design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of a new series of morpholine-benzimidazole-oxadiazole derivatives as potential anticancer agents. The anticancer potential of the synthesized derivatives was assessed through MTT assays against the human colon cancer cell line (HT-29) and normal fibroblast cells (NIH3T3) to evaluate their selectivity. To further investigate their mechanism of action, VEGFR-2 enzyme inhibition assays were conducted, as VEGFR-2 plays a crucial role in angiogenesis and tumor progression. Compound 5h exhibited potent VEGFR-2 inhibition (IC50 = 0.049 ± 0.002 μM), comparable to the reference drug sorafenib (IC50 = 0.037 ± 0.001 μM), while compounds 5j (IC50 = 0.098 ± 0.011 μM) and 5c (IC50 = 0.915 ± 0.027 μM) also showed notable inhibitory effects. Structural analysis suggested that the presence of chlorine atoms at both the third and fourth positions in the phenyl ring of compound 5h enhanced its binding affinity within the ATP-binding pocket of VEGFR-2, contributing to its potent inhibition. Moreover, in silico studies (molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations) confirmed that compounds 5c, 5h, and 5j effectively interact with the VEGFR-2 active site and exhibit stability throughout the simulation period, reinforcing their potential as sustained VEGFR-2 inhibitors. These results highlight the promising therapeutic potential of morpholine-benzimidazole-oxadiazole derivatives as selective VEGFR-2 inhibitors for the treatment of colon cancer.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures











References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
