Evaluation of Ki-67 expression levels in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using dual-energy CT quantitative parameters
- PMID: 40852477
- PMCID: PMC12367494
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1561256
Evaluation of Ki-67 expression levels in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma using dual-energy CT quantitative parameters
Abstract
Aim: This study investigates the use of dual-energy computed tomography (DECT) quantitative parameters to assess Ki-67 expression levels in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC).
Methods: A total of 57 ESCC patients who underwent dual-phase DECT scans were included. Key parameters measured were iodine concentration (IC), water concentration (WC), normalized iodine concentration (NIC), spectral Hounsfield unit curve slope (λHu), and effective atomic number (Zeff). Univariate and multivariate analyses identified factors associated with Ki-67 expression levels.
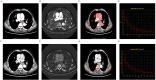
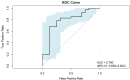
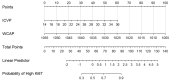
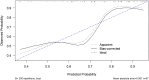
Results: Results showed that high Ki-67 expression correlated with significantly higher Zeff and IC values in the venous phase (VP) (P = 0.047 and P = 0.049, respectively; AUC = 0.67 for both), and lower WC in the arterial phase (AP) (P = 0.021; AUC = 0.70). Multivariate analysis revealed that IC in VP and WC in AP were independent predictors of Ki-67 overexpression. The combination of these two parameters yielded an AUC of 0.78 for predicting Ki-67 overexpression, with 68.3% sensitivity, 87.5% specificity, and 73.7% accuracy.
Conclusions: DECT parameters demonstrate potential for non-invasive Ki-67 status detection in ESCC, offering valuable insights for clinical diagnosis and prognosis.
Keywords: Ki-67 expression; dual-energy CT (DECT); esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; nomogram; quantitative parameters.
Copyright © 2025 Sun, Huang, Lu, Chen, Ruan and Zheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

