Case Report: A rare case of ALK-KIF5B gene fusion benefited from treatment with lorlatinib
- PMID: 40852483
- PMCID: PMC12368777
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1594072
Case Report: A rare case of ALK-KIF5B gene fusion benefited from treatment with lorlatinib
Abstract
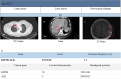
The anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene encodes a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase. Most mutations in ALK gene result from translocations with other genes, forming fusion oncogenes. To date, 21 different genes have been identified as ALK fusion partners, each activating distinct signaling pathways that influence cancer cell proliferation, invasiveness, and tumorigenicity. ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (ALK-TKIs) have demonstrated significant efficacy in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and are widely utilized as first-line therapy. Lorlatinib, a third-generation ALK inhibitor, is effective in both treatment-naïve and previously treated patients with advanced NSCLC, exhibiting strong systemic and intracranial antitumor activity. This report presented a case of lung adenocarcinoma with 51 genetic variants, including a rare fusion variant: exon 15 of KIF5B fused to exon 20 of ALK, KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20). Following lorlatinib treatment, partial remission was achieved, and disease stability was maintained for an extended period, suggesting a favorable response to therapy. This case highlighted the potential sensitivity of the KIF5B-ALK (K15:A20) fusion to lorlatinib and the need for further investigation into lorlatinib's efficacy across different KIF5B-ALK fusion variants. Additionally, other fusion types and treatment options for KIF5B-ALK fusions with varying breakpoints were discussed.
Keywords: KIF5B-ALK gene fusion; anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors; case report; loratinib; non-small cell lung cancer.
Copyright © 2025 Luo and Ouyang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous