Inferior Outcomes of Posterior Correction and Fusion Surgery for Adults With Residual Lenke Type 5 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Comparative Study With Adolescents
- PMID: 40852746
- PMCID: PMC12378117
- DOI: 10.1177/21925682251371620
Inferior Outcomes of Posterior Correction and Fusion Surgery for Adults With Residual Lenke Type 5 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: A Comparative Study With Adolescents
Abstract
Study DesignRetrospective cohort study.ObjectiveThis study aimed to determine whether the outcomes of posterior correction and fusion surgery (PSF) in patients with residual adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) during adulthood (Lenke type 5 AdIS) are inferior to those in patients with AIS treated during adolescence.MethodsWe retrospectively evaluated 48 patients with type 5 AdIS who underwent PSF after 20 years old. As controls, we selected 67 patients with type 5 AIS who underwent PSF before 18 years old. Both groups were matched based on the preoperative thoracic and thoracolumbar/lumbar Cobb angles, resulting in 33 patients in each group. We compared preoperative and postoperative radiographic parameters and SRS-22 scores between the 2 groups.ResultsPreoperatively, the AdIS group had significantly lower flexibility index (59.0% ± 13.0% vs 66.6% ± 16.7%; P = 0.01). The preoperative SRS-22 scores for pain and mental health domain were significantly worse in the AdIS group (pain, 3.9 ± 0.8 vs 4.3 ± 0.7, P < 0.01; mental health, 3.6 ± 0.8 vs 4.2 ± 0.6, P < 0.01). The AdIS group had significantly more fused vertebrae and longer intraoperative time than the AIS group. Postoperatively, lumber Cobb angle (16.1° ± 5.6° vs 8.6° ± 4.0°, P < 0.01) and correction rate were both less favorable in the AdIS group. Both pain and mental health scores remained significantly worse in the AdIS group (pain: AdIS, 4.3 ± 0.6 vs AIS, 4.7 ± 0.3; P < 0.01; mental health: AdIS, 4.1 ± 0.7 vs AIS, 4.5 ± 0.5; P = 0.02).ConclusionPatients with type 5 AdIS had a similar correction of the major curve as those with AIS; however, the surgery was more invasive, with inferior postoperative clinical outcomes, than those with AIS. These findings suggest that the surgical timing should be carefully considered in patients with type 5 AIS to optimize outcomes.
Keywords: Lenke type 5 adult idiopathic scoliosis; SRS-22 score; adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; adult patients with residual adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; intervertebral disc degeneration; lowest instrumented vertebrae; pain; thoracolumbar/lumbar curve.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
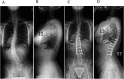
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased Surgical Invasiveness but Favorable Scoliosis Research Society-22 Scores in Adult Idiopathic Scoliosis with Major Thoracic Curves: A Comparative Study with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis.Spine Surg Relat Res. 2025 Mar 7;9(4):453-459. doi: 10.22603/ssrr.2024-0299. eCollection 2025 Jul 27. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40786930 Free PMC article.
-
What Are the Medium-term Reciprocal Changes in Cervical Sagittal Alignment After Posterior Correction for Lenke 5C Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis?Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Mar 21;483(9):1746-1758. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003448. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40117516
-
How Does Anterior Vertebral Body Tethering Compare to Posterior Spinal Fusion for Thoracic Idiopathic Scoliosis? A Nonrandomized Clinical Trial.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025 Jun 19. doi: 10.1097/CORR.0000000000003575. Online ahead of print. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2025. PMID: 40537949
-
Adult versus adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery: a meta-analysis of clinical and radiographic outcomes.Eur Spine J. 2024 Apr;33(4):1637-1643. doi: 10.1007/s00586-024-08177-x. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Eur Spine J. 2024. PMID: 38436875
-
Patient and surgical predictors of 3D correction in posterior spinal fusion: a systematic review.Eur Spine J. 2023 Jun;32(6):1927-1946. doi: 10.1007/s00586-023-07708-2. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Eur Spine J. 2023. PMID: 37079078
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

