A Photoresponsive Hybrid of Viruses and Supramolecular Peptide Fibers for Multidimensional Control of Patterning and Infection
- PMID: 40852784
- PMCID: PMC12501715
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202508528
A Photoresponsive Hybrid of Viruses and Supramolecular Peptide Fibers for Multidimensional Control of Patterning and Infection
Abstract
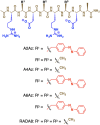
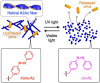
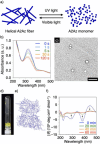
Viruses are versatile colloidal materials in their biofunctions, monodispersed and periodic structures, and high surface designability. For expanding the applicability of virus-based materials, spatiotemporally controlled immobilization and dispersion of viruses with retained activity should be useful, though control of the dynamic nature of viruses hybridized with commonly used polymers has been difficult due to their strong interactions. Here, we report a self-assembling peptide (A2Az) enabling photo control of adhesion and dispersion of M13 bacteriophage virus (M13 phage) and successfully demonstrate patterning of localization and infection of the virus. A2Az is a cationic peptide with amphiphilicity that consists of eight amino acid residues containing a photo-responsive azobenzene group at the second position and self-assembles into a helical supramolecular fiber to form a hydrogel. The helical fibrillar morphology of A2Az exhibits strong interaction with M13 phage, allowing for immobilization not only on a two-dimensional surface but also in a three-dimensional hydrogel with suppression of infectivity. The A2Az fiber undergoes a light-triggered fiber-to-particle transition and releases the immobilized M13 phage with retained infectivity for the photo-controlled patterning of localization and infection. This approach has potential applicability to various virus-based biomaterials, such as structural materials and materials for photo-selective gene transfection to cells.
Keywords: Gels; Peptides; Polymers; Supramolecular chemistry; Viruses.
© 2025 The Author(s). Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- JPMXP1224UT0073/Advanced Research Infrastructure for Materials and Nanotechnology in Japan
- Japan Society for the Promotion of Science
- JP21H05096/Grant-in-Aid for Transformative Research Areas (B)
- 23W1M041/New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization
- JPMJAX23DL/ACT-X
- JPMJCR19S4/Core Research for Evolutional Science and Technology
- JPMJFR2122/Fusion Oriented Research for Disruptive Science and Technology
- Japan Association for Chemical Innovation
- Tanaka Foundation
- Urakami Foundation for Food and Food Culture Promotion
- Kose Cosmetology Foundation
- Asahi Glass Foundation
- Toyota Riken Foundation
- Canon Foundation
- Lotte Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

