Interaction of coexposure to inorganic arsenic and manganese: Tight junction injury of the blood-brain barrier and the relationship between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in glial cells
- PMID: 40853884
- PMCID: PMC12377611
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330287
Interaction of coexposure to inorganic arsenic and manganese: Tight junction injury of the blood-brain barrier and the relationship between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in glial cells
Abstract
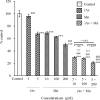
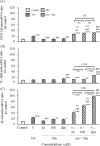
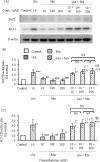
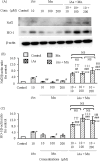
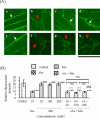
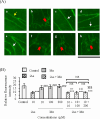
Coexposure to inorganic arsenic (iAs) and manganese (Mn) may exacerbate cognitive dysfunction caused by iAs alone. In this study, we investigated the cytotoxicity of coexposure to iAs and Mn in glial cells and the expression and correlation between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines. Additionally, we assessed tight junction (TJ) injury using a rat in vitro blood-brain barrier (BBB) model. In glial cells, coexposure to iAs and Mn increased cytotoxicity compared to single exposure, suggesting a likely additive effect. iAs exposure significantly increased the expression of antioxidant stress markers, including nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), relative to Mn exposure. Notably, HO-1 expression was further elevated under coexposure conditions, indicating a potential synergistic effect. Regarding inflammatory cytokines, expression of C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (MCP-1) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) was slightly higher in the iAs exposure compared to Mn exposure. A synergistic effect was observed in the Mn concentration-dependent increase in IL-6 under coexposure. A significant positive correlation was found between Nrf2 or HO-1 and inflammatory cytokines (MCP-1 and IL-6) (p < 0.001), suggesting an interaction between oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines. The BBB TJ injury was evaluated by measuring the transendothelial electrical resistance values and the Claudin-5 and zonula occludens-1. The results showed expression in iAs exposure but not in Mn exposure. Furthermore, Mn did not affect iAs-induced TJ injury. In conclusion, our findings demonstrate that coexposure to iAs and Mn exerts synergistic effects on oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines in glial cells. These joint effects may increase the risk of neurotoxicity compared to single-iAs or Mn exposure.
Copyright: © 2025 Hitomi et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Manju R, Hegde AM, Parlees P, Keshan A. Environmental Arsenic Contamination and Its Effect on Intelligence Quotient of School Children in a Historic Gold Mining Area Hutti, North Karnataka, India: A Pilot Study. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2017;8(3):364–7. doi: 10.4103/jnrp.jnrp_501_16 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

