Detection of Human Brain Cancers using Genomic and Immune Cell Characterization of Cerebrospinal Fluid through CSF-BAM
- PMID: 40854146
- PMCID: PMC12380150
- DOI: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-1788
Detection of Human Brain Cancers using Genomic and Immune Cell Characterization of Cerebrospinal Fluid through CSF-BAM
Abstract
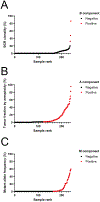
Patients with radiographically detectable lesions in their brain or other symptoms compatible with brain tumors pose challenges for diagnosis. The only definitive way to diagnose such patients is through brain biopsy, an invasive and dangerous procedure. In this study, we present a new workflow termed "CSF-BAM" that simultaneously identifies B-cell or T-cell receptor sequences, aneuploidy, and mutations using amplification of both strands of the DNA from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples. We applied CSF-BAM to a validation set of 209 samples from patients with brain cancers. Among the 129 samples from patients with the most common aggressive cancer types, the sensitivity of detection was 81%. None of 30 CSF-BAM assays were positive in CSF samples from patients without brain cancers (100% specificity). CSF-BAM provides an integrated approach to identify neoplasia in the central nervous system, provides information about the genetics and immune environment, and has the potential to inform patient management.
Significance: There is a paucity of technologies beyond surgical biopsy that can accurately diagnose central nervous system neoplasms. We developed a novel, sensitive, and highly specific assay that can detect brain cancers by comprehensively identifying somatic mutations, chromosomal copy-number changes, and adaptive immunoreceptor repertoires from samples of CSF. See related commentary by Weiss, p. 1976.
©2025 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
C.M.J. is a cofounder of Egret therapeutics with equity interests in the company and has received research support from Grifols, Biohaven, and InCephalo. E.M.J. is a consultant to Integra Lifesciences. K.C.S. reports consulting for Springworks, Nurix Therapeutics, and Novartis and research funding to Johns Hopkins from Fore Biotherapeutics, Springworks Therapeutics, and Lantern Pharma. C.H.S. and S.R. are consultants to Kiowa Kirin. C.H.S. has served on advisory boards for Acrotech Biopharma. C.H.S. has received honoraria from Medical Logix and Haymarket Medical Education. J.N. reports disclosures for AstraZeneca: research funding, consulting/advisory board, data safety monitoring board, honoraria; Bristol Myers Squibb: research funding, consulting/advisory board, data safety monitoring board, honoraria; Roche/Genentech: research funding, consulting/advisory board, honoraria; Amgen: research funding, consulting/advisory board; Arcus Biosciences: research funding, consulting/advisory board/steering committee; Mirati: research funding, honoraria; Novartis: research funding; Takeda research funding, consulting/advisory board; Pfizer: research funding, consulting/advisory board; Daiichi Sankyo: consulting/advisory board, data safety monitoring board, honoraria; NGM Pharmaceuticals: consulting/advisory board; Bayer: consulting/advisory board; Regeneron: consulting/advisory board; Elevation Oncology: consulting/advisory board; Abbvie: consulting/advisory board; Kaleido Biosciences: consulting/advisory board. P.A.C is a principal investigator on grants to Johns Hopkins University from Genentech. P.A.C. has received consulting honoraria for serving on scientific advisory boards for Biogen, Novartis, and Lilly. M.F.K. is a consultant to Allogene, Argenx, Atara Biotherapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Revel Pharmaceuticals, Sana Biotechnology, and Sanofi. M.F.K. receives research support from Blackbird Labs. S.P. is a consultant to Merck, owns equity in Gilead and received payments from IQVIA and Curio Science. B.V., K.W.K., and N.P. are founders of Thrive Earlier Detection, an Exact Sciences Company. K.W.K., N.P., and C.D. are consultants to Thrive Earlier Detection. B.V., K.W.K., N.P., and C.D. hold equity in Exact Sciences. N.P. and C.D. are consultants to Thrive Earlier Detection. B.V., K.W.K., J.D.C., and N.P. are founders of and own equity in Haystack Oncology. B.V., K.W.K., and N.P. are founders of and own equity in ManaT Bio. K.W.K. and N.P. are consultants to Neophore. K.W.K., B.V., and N.P. hold equity in and are consultants to CAGE Pharma. B.V. is a consultant to and holds equity in Catalio Capital Management. C.B. is a consultant to Depuy-Synthes, Bionaut Labs, Haystack Oncology, and Privo Technologies. C.B. is a cofounder of OrisDx. C.B. and C.D. are cofounders of Belay Diagnostics. The companies named above, as well as other companies, have licensed previously described technologies related to the work described in this paper from Johns Hopkins University. B.V., K.W.K., N.P., C. B., C.D., J.D.C., Y.W., and A.H.P. are inventors on some of these technologies. Licenses to these technologies are or will be associated with equity or royalty payments to the inventors and to Johns Hopkins University. Patent applications on the work described in this paper may be filed by Johns Hopkins University. The terms of all these arrangements are being managed by Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures


Update of
-
Detection of human brain cancers using genomic and immune cell characterization of cerebrospinal fluid through CSF-BAM.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Feb 12:2024.12.02.24318303. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.02.24318303. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Cancer Discov. 2025 Oct 6;15(10):2002-2018. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-24-1788. PMID: 39677487 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM136577/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA006973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR048522/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA276221/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI176764/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA270403/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA230691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 TR004059/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA230400/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- Alex's Lemonade Stand Foundation for Childhood Cancer (ALSF)
- Scholar Award/American Society of Hematology (ASH)
- 80049589/Benjamin Baker Endowment
- Career Award for Medical Scientists/Burroughs Wellcome Fund (BWF)
- Commonwealth Fund (CF)
- Conrad N. Hilton Foundation (CNHF)
- Cupid Foundation
- W81XWH-21-1-0251/U.S. Department of Defense (DOD)
- Career Development Award/Doris Duke Charitable Foundation (DDCF)
- Jerome Greene Foundation
- Scholar and Discovery Awards/Jerome Greene Foundation
- Translational Research Program Award/Leukemia and Lymphoma Society (LLS)
- Lustgarten Foundation (Lustgarten)
- CA06973/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- DRP80057309/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- K08CA270403/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- RA37CA230400/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R01CA276221/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- R21TR004059/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 1R21AI176764-01/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- T32AR048522/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- T32GM136577/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- U01CA230691/National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- Sol and Lillian Goldman Family Foundation
- Sol Goldman Sequencing Facility at Johns Hopkins
- Translational Cancer Research Award/Swim Across America (SAA)
- Thomas M. Hohman Memorial Cancer Research Fund
- Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research (D.K. Ludwig Fund)
- Jennison Family Funds
- Reza Khatib Brain Tumor Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

