Comparative evaluation of two herbal formulas for gastrointestinal function and gut microbiota modulation in rats with loperamide-induced dyspepsia
- PMID: 40854940
- PMCID: PMC12379153
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-15574-9
Comparative evaluation of two herbal formulas for gastrointestinal function and gut microbiota modulation in rats with loperamide-induced dyspepsia
Abstract
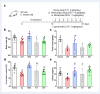
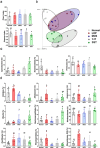
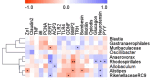
Dyspepsia is a prevalent refractory condition that arises from various causes and lacks definitive treatment. There is an urgent need for evidence to support the use of herbal medicines in the treatment of gastroenterological disorders. This study aimed to compare the therapeutic effects of two common herbal formulas-namely, Shihosogan-tang (SST) and Yijung-tang (YJT)-on loperamide (LOP)-induced dyspepsia and to explore their potential mechanisms. A dyspepsia model was established using Sprague-Dawley rats by intraperitoneal LOP injection at a dose of 3 mg/kg/day for one week. During this period, 30% ethanol extract of SST (1.4 g/kg/day) or YJT (2 g/kg/day) was intragastrically administered in rats. Mosapride (3 mg/kg/day) was used as the positive control. Unlike YJT, SST significantly mitigated LOP-induced reductions in intestinal length, gastrointestinal transit ratio, and serum ghrelin levels. Conversely, YJT significantly enhanced defecation, ileum villus length, and muscular thickness, outperforming SST. Expression of genes related to intestinal motility (ZO-1), inflammation (IL-6), and water absorption (SERT, AQP-3) indicated that both treatments ameliorated LOP-induced changes in the duodenum. Additionally, neuropeptides and hormones (TRH, bombesin, motilin, glucagon, neurotensin, PYY), Toll-like receptors (TLR-2 and TLR-4), and growth factors (GDNF and BMP2) were noticeably altered by SST and/or YJT treatment. While neither LOP nor the herbal formulas affected gut microbiota α-diversity, SST and YJT altered β-diversity compared to LOP alone, unlike mosapride. SST improves dyspepsia more effectively than YJT, possibly through mechanisms involving intestinal hormone regulation, inflammation inhibition, and gut microbiota modulation.
Keywords: Dyspepsia; Gastrointestinal motility; Ghrelin; Gut microbiota; Herbal formula.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Puerarin-rich compound Puerariae lobatae formulas alleviate hyperuricemia in mice by enhancing renal and intestinal function through regulating gut microbiota.Phytomedicine. 2025 Oct;146:157115. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.157115. Epub 2025 Aug 12. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40815946
-
Ameliorative Effects of Soybean Powder Fermented by Bacillus subtilis on Constipation Induced by Loperamide in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 6;26(15):7615. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157615. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806742 Free PMC article.
-
NTP Developmental and Reproductive Toxicity Technical Report on the Prenatal Development Studies of 2-((1-(4-Phenoxyphenoxy)propan-2-yl)oxy)pyridine (CASRN 95737-68-1) in Sprague Dawley (Hsd:Sprague Dawley® SD®) Rats and New Zealand White (Hra:NZW SPF) Rabbits: DART Report 07 [Internet].Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. Research Triangle Park (NC): National Toxicology Program; 2022 Jan. PMID: 35593777 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
The Black Book of Psychotropic Dosing and Monitoring.Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024 Jul 8;54(3):8-59. Psychopharmacol Bull. 2024. PMID: 38993656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bharucha, A. E., Dorn, S. D., Lembo, A. & Pressman, A. American gastroenterological association medical position statement on constipation. Gastroenterology144, 211–217. 10.1053/j.gastro.2012.10.029 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Lacy, B. E., Weiser, K. T., Kennedy, A. T., Crowell, M. D. & Talley, N. J. Functional dyspepsia: The economic impact to patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther.38, 170–177. 10.1111/apt.12355 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Roerig, J. L., Steffen, K. J., Mitchell, J. E. & Zunker, C. Laxative abuse: Epidemiology, diagnosis and management. Drugs70, 1487–1503. 10.2165/11898640-000000000-00000 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Sabiu, S. & Ashafa, O. T. A. Toxicological implications and laxative potential of ethanol root extract of Morella serrata in loperamide-induced constipated Wistar rats. Pharm. Biol.54, 2901–2908. 10.1080/13880209.2016.1193885 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

