Optimizing brain stroke detection with a weighted voting ensemble machine learning model
- PMID: 40855246
- PMCID: PMC12378966
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-14358-5
Optimizing brain stroke detection with a weighted voting ensemble machine learning model
Abstract
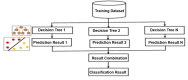
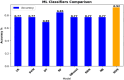
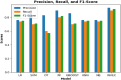
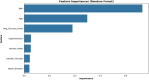
Brain stroke is a medical trauma that occurs when there is an impairment or decrease in blood circulation to a particular part of the brain, causing adjacent brain cells to die. Stroke diagnosis after an event is an ineffective method; other more labour-intensive and costly procedures exist for stroke diagnosis. This method involves directing a machine learning algorithm to a marked dataset to identify samples and irregularities indicative of stroke occurrence. This study focused on developing an ensemble machine learning model to predict brain stroke. The model combined the predictions of multiple individualistic classifiers, including random forest, eXtreme gradient boosting, and histogram-based gradient boosting, to improve accuracy. The proposed weighted voting-based ensemble (WVE) classifier model achieved an accuracy of 92.31% on a private stroke prediction dataset. The pre-assessment of stroke risk diagnosis, as suggested in this study, enables many people to take preventive actions well in advance, thereby lowering fatal effects. Our proposed method presents a feasible option for the early or initial diagnosis of stroke, as traditional methods, such as computed tomography (CT) scans and magnetic resonance imaging (MRIs), are time-consuming and costly. Future research could explore the use of intelligence-based optimization to enhance classification accuracy and address this limitation.
Keywords: Brain stroke detection; EXtreme gradient boosting (XGBoost); Histogram-based gradient boosting (HGB); Machine learning (ML); Random forest (RF); Weighted voting.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethics: A statement to confirm that all the methods and experiments conducted were purely computational and did not involve any human subjects directly. The names and personal details of the patients were highly confidential. All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. All experimental protocols were approved by the KC Multi specialty Hospital in Chennai, India. Consent for publication: We confirm that informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s).
Figures






Similar articles
-
A Weighted Voting Approach for Traditional Chinese Medicine Formula Classification Using Large Language Models: Algorithm Development and Validation Study.JMIR Med Inform. 2025 Jul 24;13:e69286. doi: 10.2196/69286. JMIR Med Inform. 2025. PMID: 40705933 Free PMC article.
-
Supervised Machine Learning Models for Predicting Sepsis-Associated Liver Injury in Patients With Sepsis: Development and Validation Study Based on a Multicenter Cohort Study.J Med Internet Res. 2025 May 26;27:e66733. doi: 10.2196/66733. J Med Internet Res. 2025. PMID: 40418571 Free PMC article.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using SonoVue® (sulphur hexafluoride microbubbles) compared with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the characterisation of focal liver lesions and detection of liver metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2013 Apr;17(16):1-243. doi: 10.3310/hta17160. Health Technol Assess. 2013. PMID: 23611316 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning is changing osteoporosis detection: an integrative review.Osteoporos Int. 2025 Aug;36(8):1313-1326. doi: 10.1007/s00198-025-07541-x. Epub 2025 Jun 10. Osteoporos Int. 2025. PMID: 40493238 Review.
References
-
- Polat, Ö., Dokur, Z. & Ölmez, T. Classification of brain strokes using divergence-based convolutional neural networks. Biomed. Signal Process. Control93, 106193. 10.1016/j.bspc.2024.106193 (2024).
-
- Goni, M. R., Ruhaiyem, N. I. R., Mustapha, M., Achuthan, A. & Che Mohd Nassir, C. M. N. Brain vessel segmentation using deep learning—a review. IEEE Access10, 111322–111336. 10.1109/access.2022.3214987 (2022).
-
- Baek, H. et al. Deep cerebellar low-intensity focused ultrasound stimulation restores interhemispheric balance after ischemic stroke in mice. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng.28(9), 2073–2079. 10.1109/tnsre.2020.3002207 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Guo, T. et al. Pulsed transcranial ultrasound stimulation immediately after the ischemic brain injury is neuroprotective. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.62(10), 2352–2357. 10.1109/tbme.2015.2427339 (2015). - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

