Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of Osimertinib-Cy7 (OSA-Cy7) conjugate as potential theranostic agent targeting activating EGFR mutations
- PMID: 40855276
- PMCID: PMC12379436
- DOI: 10.1186/s12896-025-01025-w
Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of Osimertinib-Cy7 (OSA-Cy7) conjugate as potential theranostic agent targeting activating EGFR mutations
Abstract
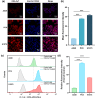
Accurately predicting the therapeutic response of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients to tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) is of significant clinical importance. The use of TKIs in clinical is primarily guided by the detection of EGFR gene mutations. However, the current EGFR mutation assays face challenges such as inconsistent correlation with therapeutic outcomes, inconvenient sample availability and limited sensitivity. To address these, we have designed and synthesized a novel theranostic agent, OSA-Cy7, by conjugating the third-generation EGFR-TKI osimertinib with the near-infrared (NIR) fluorophore Cy7. This conjugate aims to enable fluorescence-based detection of mutant EGFR and targeted therapy of NSCLC. Our studies demonstrated that OSA-Cy7 selectively accumulates in EGFR-mutant NSCLC cell lines, such as PC9 (exon 19 deletion) and H1975 (L858R/T790M), exhibiting enhanced fluorescence signals, while showing minimal uptake in wild-type EGFR A549 cells. Western blot analysis confirmed that OSA-Cy7 effectively inhibits EGFR phosphorylation in mutant cell lines, with negligible effects on wild-type EGFR phosphorylation. Furthermore, OSA-Cy7 treatment resulted in significant suppression on cell proliferation and colony formation in EGFR-mutant cells, indicating its potent anticancer activity. These findings suggest that OSA-Cy7 holds promise as a theranostic agent for the selective imaging and treatment of EGFR-mutant NSCLC, potentially improving patient stratification and therapeutic monitoring.
Keywords: EGFR mutation dectection; Fluorescence-based assay; NSCLC; Osimertinib; TKI response evaluation; Theranostic agent.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study did not involve human participants, animals, human tissue, human data, or clinical trials. All cell lines were obtained from commercial repositories and used under standard laboratory protocols. Ethical approval was not required for this research and compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki was not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

