Eravacycline use in immunocompromised patients: multicenter evaluation of timely versus late initiation on clinical outcomes
- PMID: 40856499
- PMCID: PMC12502764
- DOI: 10.1128/spectrum.00565-25
Eravacycline use in immunocompromised patients: multicenter evaluation of timely versus late initiation on clinical outcomes
Abstract
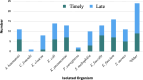
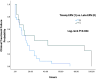
Infections from multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria lead to worse outcomes in immunocompromised patients. Eravacycline (ERV) is effective against MDR gram-negative and gram-positive bacteria, but its effects in immunocompromised populations remain unstudied. We aimed to evaluate clinical end points of immunocompromised patients receiving timely versus late ERV therapy. This multicenter, retrospective, observational study (October 2018 to September 2022) included adult immunocompromised patients hospitalized and treated with ERV for ≥72 h. The primary outcome was a composite of all-cause 30-day mortality, failure to improve clinically while on ERV, and/or microbial recurrence within 30 days of ERV initiation. Inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) and Kaplan-Meier analyzes were used. Eighty-two patients from 17 US centers were included (median age 62 years; 59% male; intensive care unit admissions 57%). In the unadjusted cohort, timely ERV significantly reduced odds of clinical treatment failure (odds ratio [OR]: 0.321, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.129-0.800, P = 0.012) and microbial recurrence (OR: 0.545, 95% CI: 0.326-0.913, P = 0.034) compared to late ERV; in the IPTW-adjusted cohort, these associations remained significant with ORs of 0.675 (95% CI: 0.465-0.979, P = 0.029) for treatment failure and 0.384 (95% CI: 0.142-0.943, P = 0.041) for recurrence. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed a higher cumulative proportion of clinical treatment failure in the late ERV group (57%) compared to the timely ERV group (30%, P = 0.013), with a significantly longer time to clinical treatment failure in the timely ERV group (log-rank P = 0.034). Timely initiation of ERV in immunocompromised patients may improve clinical outcomes by reducing treatment failure and microbial recurrence compared to later initiation.IMPORTANCEThis multicenter, retrospective study evaluates the impact of timely versus late initiation of eravacycline (ERV) in immunocompromised patients with multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Immunocompromised patients face heightened risks of severe infections due to weakened immune defenses and limited treatment options, yet data on ERV use in this population are scarce. Our findings demonstrate that timely ERV initiation ≤72 h from index culture collection) significantly reduces clinical treatment failure and microbial recurrence compared to late initiation, with inverse probability of treatment weighting-adjusted odds ratios of 0.675 (P = 0.029) for treatment failure and 0.384 (P = 0.041) for recurrence. Kaplan-Meier analysis further confirms that delayed ERV therapy is associated with a higher cumulative incidence of clinical failure (57% vs 30%, P = 0.013). These results highlight the importance of early ERV initiation in optimizing outcomes for immunocompromised patients and addressing the growing challenge of MDR infections, emphasizing the need for further prospective studies to confirm these findings.
Keywords: antimicrobial stewardship; eravacycline; immunocompromised; multidrug-resistant.
Conflict of interest statement
S.A. is a current employee of Agios Pharmaceuticals. T.M. is currently receiving grant funding through Stellus Rx and AbbVie, Inc., has participated in scientific advisory boards for AbbVie Inc. and Basilea Pharmaceutica, has provided expert witness testimony for Copeland, Stair Valz & Lovell, and has received honorarium from Infectious Diseases Special Edition. J.A. is a speaker for Shionogi Inc. M.A.K. is a speaker for Tetraphase. M.P.V. received research funding from Paratek Pharmaceuticals, Cumberland Pharmaceuticals, NIAID, and advisory Boardsboards for Ferring Pharmaceuticals, Melinta Therapeutics, and Merck & Co. K.C.M. has received research and consulting from or participated in speaking bureaus for Shionogi, Innoviva Therapeutics, Melinta, and Merck. A.L.V.H. has participated in speaking bureaus and has received research funding from Tetraphase. S.L.K.-B. is a consultant for Allergan, Spero, and Tetraphase. M.J.R. has received research and consulting from or participated in speaking bureaus for AbbVie, Melinta, Merck, Paratek, Shionogi, T2 Biosystems, and Tetraphase (La Jolla, Innovia) and is partially supported by NIAID R21 AI163726 and R01AI130056. All other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gaibani P, Giani T, Bovo F, Lombardo D, Amadesi S, Lazzarotto T, Coppi M, Rossolini GM, Ambretti S. 2022. Resistance to ceftazidime/avibactam, meropenem/vaborbactam and imipenem/relebactam in Gram-negative MDR Bacilli: molecular mechanisms and susceptibility testing. Antibiotics (Basel) 11:628. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11050628 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jolles S, Smith BD, Vinh DC, Mallick R, Espinoza G, DeKoven M, Divino V. 2022. Risk factors for severe infections in secondary immunodeficiency: a retrospective US administrative claims study in patients with hematological malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma 63:64–73. doi: 10.1080/10428194.2021.1992761 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

