Enhancing the early detection of Alzheimer's disease using an integrated CNN-LSTM framework: A robust approach for fMRI-based multi-stage classification
- PMID: 40857304
- PMCID: PMC12380340
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0317968
Enhancing the early detection of Alzheimer's disease using an integrated CNN-LSTM framework: A robust approach for fMRI-based multi-stage classification
Abstract
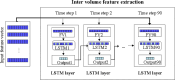
Alzheimer's Disease poses a significant challenge as a progressive and irreversible neurological condition striking the elderly population. Its incurable nature correlates with a significant rise in death rates. However, early detection can slow its progression and facilitate prompt intervention, thereby mitigating mortality risks. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) provides valuable insights into the functional changes within distinct brain regions associated with the disease. The recent research efforts have extracted functional connectivity measures for the classification. These handcrafted functional connectivity features are usually not robust and are computationally intensive. To address the issue, this study introduces an integrated deep-learning framework based on CNN and LSTM networks. This framework autonomously learns both intra-volume and inter-volume features critical for classification tasks. CNNs facilitate feature extraction, while LSTM networks govern the selection of significant features for classification. The key aim of this study is to classify Alzheimer's disease and its prodromal stage, Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). MCI is further categorized as early MCI (EMCI) and late MCI (LMCI). We have evaluated the framework in three dimensions, binary classification, multi-class classification with 3-classes, and multi-class classification with 4-classes. For each dimension, multiple classifications were performed. The results depict the proposed CNN-LSTM framework to attain 99% accuracy and 100% average area under the curve for the majority of the classification.
Copyright: © 2025 Farhan et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
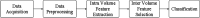


Similar articles
-
Predicting cognitive decline: Deep-learning reveals subtle brain changes in pre-MCI stage.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 May;12(5):100079. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2025.100079. Epub 2025 Feb 6. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 39920001 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Validation of a Brain Aging Biomarker in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: Deep Learning Approach.JMIR Aging. 2025 Aug 1;8:e73004. doi: 10.2196/73004. JMIR Aging. 2025. PMID: 40750095 Free PMC article.
-
Improving early detection of Alzheimer's disease through MRI slice selection and deep learning techniques.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 10;15(1):29260. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-14476-0. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40784967 Free PMC article.
-
The application value of Rs-fMRI-based machine learning models for differentiating mild cognitive impairment from Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurol Sci. 2025 Jan;46(1):45-62. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07731-1. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39225837 Free PMC article.
-
¹⁸F-FDG PET for the early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 28;1(1):CD010632. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010632.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25629415 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Burns A, Jacoby R, Luthert P, Levy R. Cause of death in Alzheimer’s disease. Age Ageing. 1990;19(5):341–4. - PubMed
-
- Heron M. Deaths: Leading causes for 2016 ; 2018.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

