Optimization and validation of the international metabolic prognostic index for CD19 CAR-T in large B-cell lymphoma
- PMID: 40858552
- PMCID: PMC12381142
- DOI: 10.1038/s41408-025-01338-1
Optimization and validation of the international metabolic prognostic index for CD19 CAR-T in large B-cell lymphoma
Abstract
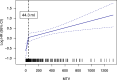
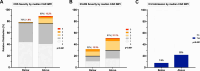
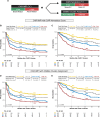
While CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapy represents a transformative immunotherapy for relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma (r/r LBCL), more than 50% of patients ultimately progress or relapse. Recently, the International Metabolic Prognostic Index (IMPI) - incorporating age, stage, and metabolic tumor volume (MTV) - was shown to improve prognostication for LBCL frontline treatment. Here, we examine its utility to predict toxicity and survival in CAR-T recipients. This multicenter observational study spanning six international sites included 504 patients with available 18FDG-PET/CT imaging at last response assessment prior to lymphodepletion. Optimal CAR-adapted MTV thresholds were identified in a development cohort (n = 256) and incorporated into a CAR-T-specific IMPI ("CAR-IMPI"). The prognostic performance of CAR-IMPI was validated in an independent cohort (n = 248). CAR-IMPI risk categories, defined by the median (1.35) and terciles (1.07, 1.58), demonstrated significant discrimination for progression-free survival (PFS; p < 0.0001) and overall survival (OS; p < 0.0001) in both cohorts. Multivariate Cox regression confirmed CAR-IMPI as an independent predictor of survival, accounting for pre-lymphodepletion LDH and CRP, performance status, treatment center, and CAR-T product. Patients in the CAR-IMPI high-risk category experienced increased severity of CRS and ICANS, and higher rates of intensive care unit (ICU) admissions. In an exploratory analysis, combining CAR-IMPI with established indices of high-risk systemic inflammation (CAR-HEMATOTOX, InflaMix) further enhanced survival stratification. The CAR-IMPI may provide a potent and validated PET-based tool for risk stratification of clinical outcomes in patients with r/r LBCL receiving CD19 CAR-T therapy. Our data highlight the utility of combining clinical and radiological modalities, with implications for patient selection and the anticipated level-of-care for toxicity management.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: M.D.J.: Consultancy/Advisory for Kite/Gilead, Novartis, and Myeloid Therapeutics. Research funding by Incyte, Kite/Gilead, and Loxo@Lilly. G.I.: Honoraria from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Kite, a Gilead Company, Miltenyi Biotec, Novartis, and Roche; consulting/advisory role for Autolus Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Kite, Miltenyi Biotec, and Novartis; and travel support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Kite and Miltenyi Biotec. F.M.: ArgoBIO Consulting; AstraZeneca Honoraria, Consulting, Research grant; BMS Honoraria, Consulting, Research Grant, CRISPR Therapeutics Consulting, EcoR1 Consulting, Janssen Honoraria, Consulting, Kite/Gilead, Honoraria, Consulting, Research Grant, Abbvie Honoraria, Incayte Honoraria, Miltenyi medicine Honoraria, MSD Honoraria, Novartis Honoraria, Consulting, Pfizer Honoraria, Sobi Honorarai, Takeda Honoraria. L.H.: Advisory Committees: Bristol Myers Squibb, Gilead, Johnson&Johnson, Pierre-Fabre, Sanofi; travel support: Amgen, Gilead, Johnson&Johnson. G.L.S.: has research funding to the institution from Janssen, Amgen, BMS, Beyond Spring, and GPCR, and is on the DSMB for ArcellX. Mi.S.: served as a paid consultant for McKinsey & Company, Angiocrine Bioscience, and Omeros; has received research funding from Angiocrine Bioscience and Omeros; has served on ad hoc advisory boards for Kite Pharma; and has received honoraria from i3Health and Medscape for CME related activity. W.G.K.: Bristol Myers Squibb: Advisor. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests. None of the mentioned conflicts of interest were related to financing of the content of this manuscript. A.P.B.: received compensation for participating in consulting activities with Bristol Myers Squibb. M.A.P.: honoraria from Adicet, Allogene, Caribou Biosciences, Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Equilium, Exevir, ImmPACT Bio, Incyte, Karyopharm, Kite/Gilead, Merck, Miltenyi Biotec, MorphoSys, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, Omeros, OrcaBio, Pierre Fabre, Sanofi, Syncopation, Takeda, VectivBio AG, and Vor Biopharma. He serves on DSMBs for Cidara Therapeutics and Sellas Life Sciences. He has ownership interests in Omeros and OrcaBio. He has received institutional research support for clinical trials from Allogene, Genmab, Incyte, Kite/Gilead, Miltenyi Biotec, Nektar Therapeutics, and Novartis. M.S.: Amgen: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Astra Zeneca: Speakers Bureau; Aven Cell: Consultancy, BMS/Celgene: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; CDR-Life: Consultancy, Gilead: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; GSK: Speakers Bureau; Ichnos Sciences: Consultancy; Incyte Biosciences: Consultancy; Janssen: Research Funding, Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Miltenyi Biotec: Research Funding, Consultancy; Morphosys: Research Funding; Molecular Partners: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding, Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Pfizer: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; Roche: Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding, Consultancy, Speakers Bureau. P.B.: Allogene, Amgen, Autolus, BMS/Celgene, Kite/Gilead, Incyte, Miltenyi Biomedicine, Novartis, Pfizer and Pierre Fabre: Honoraria, travel support and consultancy. F.L.L.: Consulting or Advisory Role: Novartis, Celgene, Calibr, Alimera Sciences, Gerson Lehrman Group, EcoR1 Capital, Amgen, Bluebird Bio, Bristol Myers Squibb, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Legend Biotech, Cowen, Kite, a Gilead company, Umoja Biopharma, Takeda, Sana Biotechnology, Daiichi Sankyo/UCB Japan, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, Janssen, A2 Biotherapeutics, Miltenyi Biotec, Caribou Biosciences. Research Funding: Kite, a Gilead company (Inst), Alimera Sciences (Inst), Novartis (Inst), Bluebird Bio (Inst), Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene (Inst). Patents, Royalties, Other Intellectual Property: Double Mutant Survivin Vaccine. US010414810B2 (Inst), CAR T Cells with Enhanced Metabolic Fitness. Serial Number: 62/939,727 (Inst), Methods of Enhancing CAR T Cell Therapies. Serial Number: 62/892,292 (Inst), Evolutionary Dynamics of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma CAR-T cell therapy. Serial Number: 62/879,534 (Inst). Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Kite, a Gilead company, A2 Biotherapeutics. R.S: Honoraria from Sanofi and Incyte. K.R.: Kite/Gilead: Research Funding, Consultancy, Honoraria and travel support; Novartis: Honoraria; BMS/Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pierre-Fabre: travel support. CSL Baehring: Consultancy. Ethics approval, consent to participate and Publication: All medical records and imaging studies were reviewed and approved by the appropriate Institutional Review Boards of each participating institution. Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. All procedures were conducted in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations, and in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anti-CD19 CAR-T Cell Therapy in Elderly Patients: Multicentric Real-World Experience from GETH-TC/GELTAMO.Transplant Cell Ther. 2024 Oct;30(10):988.e1-988.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2024.06.022. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Transplant Cell Ther. 2024. PMID: 39069076
-
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy for people with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 13;9(9):CD013365. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013365.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34515338 Free PMC article.
-
Semiquantitative PET Parameters Refine Prognosis in CAR T-Treated Lymphoma After 1 and 3 Months: A Prospective Single-Center Study.J Nucl Med. 2025 Aug 1;66(8):1183-1191. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.125.269670. J Nucl Med. 2025. PMID: 40246539 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Real-World Outcomes with Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapies in Large B Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Transplant Cell Ther. 2024 Jan;30(1):77.e1-77.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2023.10.017. Epub 2023 Oct 27. Transplant Cell Ther. 2024. PMID: 37890589
-
Outcomes of CD19 CAR-T therapy in central nervous system lymphoma: Insights from a multicentre experience.Br J Haematol. 2025 Aug;207(2):525-534. doi: 10.1111/bjh.20234. Epub 2025 Jul 1. Br J Haematol. 2025. PMID: 40589238
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, Waller EK, Borchmann P, McGuirk JP, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N. Engl J Med. 2019;380:45–56. - PubMed
-
- Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396:839–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

