TiRobot-assisted percutaneous vertebroplasty in the management of middle and upper thoracic osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
- PMID: 40859166
- PMCID: PMC12379487
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-025-03049-7
TiRobot-assisted percutaneous vertebroplasty in the management of middle and upper thoracic osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of TiRobot-assisted PVP surgery in the treatment of middle and upper thoracic OVCF. We also aimed to determine (1) changes in Visual Analog Scale (VAS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) before and after treatment, (2) imaging changes of the fractured vertebra, (3) operation time and intraoperative blood loss, (4) frequency of puncture and fluoroscopy, hospital stay, radiation exposure of patient and surgeon, and (5) bone cement leakage and distribution and operation-related complications.
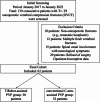
Methods: A retrospective analysis was performed on 62 patients with OVCF of the middle and upper thoracic vertebrae (T1-T8) who underwent PVP surgery in Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital from January 2017 to January 2023. Of them, 30 and 32 patients underwent TiRobot-assisted PVP surgery (robot group) and conventional C-arm-assisted PVP surgery (conventional group), respectively. VAS and ODI scores and the anterior height and local kyphotic angle of the fractured vertebra were compared before surgery and 3 days, 1 month, and 1 year after surgery. Simultaneously, the operation time, intraoperative blood loss, puncture frequency, fluoroscopy frequency, hospital stay, surgeon radiation exposure, patient radiation exposure, bone cement leakage, cement distribution, and complication were compared between the two groups.
Results: VAS score and ODI score at 3 days, 1 month, and 1 year after surgery were significantly improved in both groups compared with those before surgery (p < 0.05). The VAS score of the robot group was lower than that of the conventional group 3 days after surgery (p < 0.05), with no significant difference observed before and after surgery (p > 0.05). No significant difference was observed in anterior height and local kyphotic angle of fractured vertebra between the two groups before and after the surgery (p > 0.05). The operation time, intraoperative blood loss, puncture frequency, fluoroscopy frequency, hospital stay, surgeon radiation exposure, patient radiation exposure, bone cement leakage, and cement distribution of the robot group were all better than those of the conventional group (p < 0.05). Simultaneously, the incidence of complications in the robot group was 3.33% (1/30) lower than that of the conventional group (15.62%) (5/32) (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: Compared with traditional PVP surgery, the use of TiRobot-assisted PVP in the treatment of middle and upper thoracic OVCF has the advantages of accuracy, safety, and low-radiation exposure, which can further improve surgical safety, reduce bone cement leakage, and achieve satisfactory clinical efficacy.
Keywords: Osteoporotic compression fractures; Percutaneous vertebroplasty; Therapeutic study; Thoracic; TiRobot; Upper.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
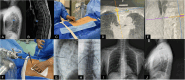
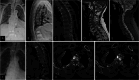
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, China (No: K2022012). All participants signed informed consent of permitting their clinical data to be used for the study. Consent for publication: The authors affirm that all participants signed informed consent of permitting their clinical data to be used for the study, and the participants provided informed consent for publication of the images in Figs. 2 and 3. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Compston JE, McClung MR, Leslie WD. Osteoporosis. Lancet. 2019;393(10169):364–76. - PubMed
-
- Lamanna A, Maingard J, Kok HK, Ranatunga D, Looby ST, Brennan P, Chua M, Owen A, Brooks DM, Chandra RV, et al. Vertebroplasty for acute painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: an update. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol. 2019;63(6):779–85. - PubMed
-
- Chang M, Zhang C, Shi J, Liang J, Yuan X, Huang H, Li D, Yang B, Tang S. Comparison between 7 osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures treatments: systematic review and network meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. 2021;145:462–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

