Synthesis of novel N1 functionalized diazepinone analogues via a base-mediated C-N cross coupling reaction as reverse transcriptase inhibitors: theoretical and experimental investigations
- PMID: 40860107
- PMCID: PMC12376879
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra03504j
Synthesis of novel N1 functionalized diazepinone analogues via a base-mediated C-N cross coupling reaction as reverse transcriptase inhibitors: theoretical and experimental investigations
Abstract
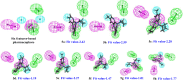
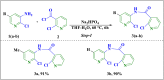
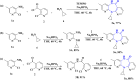
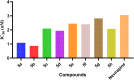
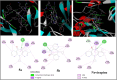
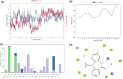
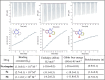
The sodium hydrogen orthophosphate (Na2HPO4) base was utilized in a stereospecific C-N coupling reaction to synthesize a novel series of nevirapine analogues in two-step reactions. This base is moisture tolerant, commercially available and makes the protocol cheap and energy efficient, with broad substrate tolerance, leading to the formation of cyclopropyl, cyclobutyl, cyclopentyl and propane-engrafted dipyridodiazepinone derivatives in good yield with a higher atom economy >70%. All the synthesized analogues were examined for reverse transcriptase inhibitory activity and compared with the reference drug nevirapine. Further in silico analysis via molecular docking, molecular simulation, and ADMET studies revealed that compounds 5a and 5b showed prominent inhibitory activity against reverse transcriptase. Additionally, isothermal titration calorimetry experiments were performed to determine the thermodynamic parameters of the interaction between nevirapine analogues and human serum albumin. The binding affinity of 5b in the order of 102 indicates that the synthesized analogues can be easily carried out into the bloodstream. These findings demonstrate that nevirapine analogous are promising reverse transcriptase inhibitors for the therapeutic treatment of HIV infection, offering a new avenue for the less toxic and more effective development of anti-retroviral drugs.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures






References
-
- Leśniewska A. Przybylski P. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024;275:116556. - PubMed
-
- Malki Y. Martinez J. Masurier N. Med. Res. Rev. 2021;41:2247–2315. - PubMed
-
- Jaiswal S. Kishore D. Bhardwaj A. Bhardwaj K. Richa S. Jain S. Dwivedi J. Sharma S. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024;22:6520–6531. - PubMed
-
- Fader L. D. Landry S. Morin S. Kawai S. H. Bousquet Y. Hucke O. Goudreau N. Lemke C. T. Bonneau P. Titolo S. Mason S. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013;23:3396–3400. - PubMed
-
- Bellarosa D. Antonelli G. Bambacioni F. Giannotti D. Viti G. Nannicini R. Giachetti A. Dianzani F. Witvrouw M. Pauwels R. Desmyter J. Antiviral Res. 1996;30:109–124. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

