The Skin-Brain Axis in Psoriasis and Depression: Roles of Inflammation, Hormones, Neuroendocrine Pathways, Neuropeptides, and the Microbiome
- PMID: 40860250
- PMCID: PMC12372838
- DOI: 10.2147/PTT.S535900
The Skin-Brain Axis in Psoriasis and Depression: Roles of Inflammation, Hormones, Neuroendocrine Pathways, Neuropeptides, and the Microbiome
Abstract
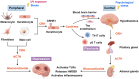
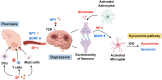
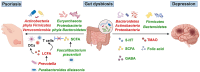
Psoriasis, a common chronic inflammatory skin disease affecting approximately 2-3% of the global population, frequently co-occurs with depression. This highly prevalent comorbidity significantly impairs patients' quality of life. Despite the substantial physical and mental health burden imposed by psoriatic depression, the underlying pathophysiological mechanisms connecting psoriasis and depression remain poorly understood. In this review, we explored several pathological processes that may contribute to psoriasis-associated depression, including immune cells dysregulations, hormones imbalances, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunctions, neuropeptides expression abnormalities, and gut dysbiosis. The primary purpose of this review was to present a comprehensive overview of the pathogenic mechanisms linking psoriasis and depression. These insights may guide trans-disciplinary interventions aimed at both skin and mood symptoms.
Keywords: HPA axis; Th17 cell; depression; gut microbiota; neuropeptides; psoriasis.
© 2025 Tang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicting interests in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Unravelling the gut-skin axis: the role of gut microbiota in pathogenesis and management of psoriasis.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jul;33(7):3671-3678. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01813-y. Epub 2025 Jun 12. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40504322 Review.
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

