Engineering Nanoparticle Surface Amphiphilicity: An Integrated Computational and Laser Desorption Ionization Study of Controlled Ligand Self-Assembly
- PMID: 40860254
- PMCID: PMC12376114
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5c03644
Engineering Nanoparticle Surface Amphiphilicity: An Integrated Computational and Laser Desorption Ionization Study of Controlled Ligand Self-Assembly
Abstract
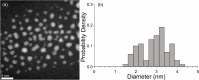
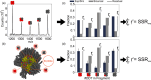
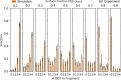
Multiligand monolayers can self-organize into advantageous interfacial patterns that govern nanoparticle (NP) properties. Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is widely incorporated into self-assembled monolayers to enhance biocompatibility, particularly in drug delivery applications. Previous studies demonstrate that monolayer phase separation can be controlled by leveraging the energetic and entropic driving forces acting on ligands in the design of amphiphilic surfaces. In this work, we extend an integrated experimental and simulation framework to investigate the self-assembly of dodecanethiol (DDT), a long hydrophobic alkanethiol, with 2-ethoxyethane-1-thiol, a short hydrophilic PEG-thiol, as a function of their surface composition on ultrasmall gold NPs. The PEG-DDT Au NPs were synthesized via ligand exchange. Integrated MALDI-MS experiments and configurationally biased Monte Carlo simulations were used to analyze and predict the local ordering of the surface ligands. The MALDI-MS fragment distributions obtained from experiment and simulation show quantitative agreement, and both indicate that the PEG-DDT ligands undergo phase separation, resulting in NP monolayers with patchy to Janus-like hydrophilic and hydrophobic ligand domains. Further, the domain size was found to increase proportionally with the surface fraction of each ligand, thereby demonstrating the ability to tune patch sizes in amphiphilic monolayers by controlling the surface composition.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
Comparison of self-administered survey questionnaire responses collected using mobile apps versus other methods.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jul 27;2015(7):MR000042. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000042.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26212714 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Memory Impairment.2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2024 Jun 8. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31424720 Free Books & Documents.
-
Electrophoresis.2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36251838 Free Books & Documents.
References
-
- Grisel R., Weststrate K.-J., Gluhoi A., Nieuwenhuys B. E.. Catalysis by Gold Nanoparticles. Gold Bulletin. 2002;35:39–45. doi: 10.1007/BF03214836. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
