Identification and experimental validation of prognostic genes related to cytochrome c in breast cancer
- PMID: 40860340
- PMCID: PMC12375475
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1627134
Identification and experimental validation of prognostic genes related to cytochrome c in breast cancer
Abstract
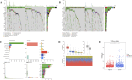
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most prevalent malignant diseases affecting women. Cytochrome c (Cyt c) plays a critical role in various pathological processes, however, its precise mechanism in BC remains unclear. This study aimed to identify prognostic genes linked to Cyt c in BC and explore their underlying mechanisms. Transcriptome data related to BC were initially obtained from TCGA and GEO database. Prognostic genes were identified through differential expression analysis, univariate Cox regression, and LASSO analysis. A risk model was subsequently developed and validated. Additionally, enrichment analysis, immune microenvironment analysis, and the construction of a TFs-mRNA network were conducted. Finally, the expression levels of prognostic genes were examined in both tumor and normal tissue samples, with confirmation through RT-qPCR. Eight prognostic genes (CETP, CLEC11A, CYP2A6, CYP2A7, GZMB, HGF, LDHC, and PLAU) were identified. The risk model demonstrated that low-risk individuals have significantly higher survival rates. GSEA results indicated that seven of the prognostic genes are notably enriched in the "cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction" pathway. Transcription factors, such as ATF3 and RUNX1, were found to regulate these prognostic genes. Furthermore, immune cell profiles revealed significant differences between high-risk and low-risk groups. Bioinformatics and RT-qPCR analyses confirmed that CETP and HGF are upregulated in normal tissues, while CLEC11A and PLAU showed higher expression in BC tissues. This study identified eight Cyt c-related prognostic genes and developed a risk model, offering new insights into personalized treatment and prognosis for BC.
Keywords: breast cancer; cytochrome c; cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction; prognostic genes; risk model.
Copyright © 2025 Yu, Li, Wu and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Aguchem R. N., Okagu I. U., Okorigwe E. M., Uzoechina J. O., Nnemolisa S. C., Ezeorba T. P. C. (2024). Role of CETP, PCSK-9, and CYP7-alpha in cholesterol metabolism: potential targets for natural products in managing hypercholesterolemia. Life Sci. 351, 122823. 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.122823 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bai Y., Xu H., Guo M., Xia L., Deng S. (2024). Extensive infiltration of CD8+ T cells and M1 macrophages is beneficial for multiple cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. MedComm – Oncol. 3 (3), e89. 10.1002/mog2.89 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

