Multifunctional Nanobody Fusion Proteins in Immunoassays: Diverse Strategies for Enhanced Analytical Performance
- PMID: 40860993
- PMCID: PMC12377495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2025.118404
Multifunctional Nanobody Fusion Proteins in Immunoassays: Diverse Strategies for Enhanced Analytical Performance
Abstract
Nanobodies, derived from camelid heavy-chain antibodies, offer exceptional specificity, stability, and solubility, enabling rapid and sensitive immunoassays. Their small size makes them ideal scaffolds for genetic fusion with reporter proteins, functional peptides, and signal amplification modules. In contrast to conventional antibodies, nanobodies can be precisely engineered at the gene level, allowing directional conjugation and efficient incorporation of signal-enhancing elements. This tunability simplifies assay design and reduces processing steps. Additionally, recombinant expression systems enable stable, scalable, and standardized production of nanobody-based immunoreagents, ensuring reproducibility in diagnostics. In this review, we summarize recent advances in the engineering and application of nanobody fusion proteins in immunoassays, with a particular focus on three main strategies: signal reporting, site-oriented strategies, and multivalency. We highlight how these approaches enhance sensitivity, shorten assay time, and enable multiplex detection. Finally, we discuss future perspectives and remaining challenges in the design and application of nanobody-based platforms for diagnostics.
Keywords: Fusion protein; Immunoassay; Immunoreagents; Nanobody; Protein tag.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest to publish this paper.
Figures

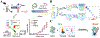




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
