Sample Ascertainment and Recruitment Sources in the Accelerating Medicines Partnership Schizophrenia Program
- PMID: 40861306
- PMCID: PMC12377801
- DOI: 10.1093/schizbullopen/sgaf013
Sample Ascertainment and Recruitment Sources in the Accelerating Medicines Partnership Schizophrenia Program
Abstract
Background: This paper presents the recruitment sources of clinical high-risk (CHR) and community controls (CC) from the Accelerating Medicines Partnership Schizophrenia (AMP SCZ) program, which aims to study various clinical variables and biomarkers in 2040 CHR and 652 CC participants.
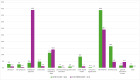
Methods: A total of 1640 CHR and 514 CC had recruitment source data. The Positive Symptoms and Diagnostic Criteria for the Comprehensive Assessment of At-Risk Mental States Harmonized with the SIPS was utilized to assess CHR criteria and severity of attenuated psychotic symptoms (APSs), and the Global Functioning: Social Scale was used for social functioning. Participants were recruited through various methods, including referrals from healthcare providers, schools, and community agencies, and self-referrals via outreach efforts and advertising.
Results: Participants were recruited from 13 different sources, with self-referral being the most common for both CHR and CC. Other notable sources included child and youth services and psychiatric hospitals and departments. Regional differences in recruitment patterns were observed across continents. Differences in age, APS, and social functioning for CHR participants were examined in the top 5 recruitment sources. Overall, self-referred individuals were typically older, with less severe APS and higher levels of functioning, whereas those from adult community mental health services had poorer functioning and more severe APS. The remaining recruitment groups fell between these 2 extremes.
Conclusion: This paper highlights the diverse recruitment sources for the AMP SCZ program. Self-referral was a significant source, particularly in North America, reflecting changing help-seeking behaviors influenced by the internet and social media. The findings underscore the importance of understanding recruitment sources to optimize future CHR research.
Keywords: AMP SCZ; ascertainment; clinical high risk; community controls; psychosis; recruitment.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the University of Maryland’s school of medicine, Maryland Psychiatric Research Center.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. C. Arango has been a consultant to and/or has received honorarium and or grants from Acadia, Angelini, Biogen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Gideon Richter, Janssen Cilag, Lundbeck, Medscape, Menarini, Minerva, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche, Sage, Servier, Shire, Shering Plough, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Sunovian, and Takeda. Dr. R. Upthegrove has received speaker fees for Otsuka and consulted to Viatris and Springer Healthcare. Dr. P. Fusar Poli has received research funds or personal fees from Angelini, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lundbeck, Menarini, Otsuka, Sunovian, and Proxymm Science. Dr. S. Woods has received speaking fees from the American Psychiatric Association and from Medscape Features. He has been granted US patent no. 8492418 B2 for a method of treating prodromal schizophrenia with glycine agonists. He owns stock in NW PharmaTech. Dr. C. Diaz-Caneja has received grant support from Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation and honoraria or travel support from Angelini, Janssen, and Viatris. Dr. Kambeitz has received speaking or consulting fees from Janssen, Boehringer Ingelheim, ROVI, and Lundbeck. Patricia J. Marcy is a consultant for Otsuka and TEVA. Dr. R. S. Kahn is a consultant for Alkermes, Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. J. Kane Consultant to or receives honoraria and/or travel support and/or speakers bureau: Alkermes, Allergan, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cerevel, Dainippon Sumitomo, H. Lundbeck, HealthRhythms, HLS Therapeutics, Indivior, Intracellular Therapies, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Johnson & Johnson, Karuna Therapeutics/Bristol Meyer-Squibb, LB Pharmaceuticals, Mapi, Maplight, Merck, Minerva, Neurocrine, Newron, Novartis, NW PharmaTech, Otsuka, Roche, Saladax, Sunovion, and Teva. Advisory Boards: Alkermes, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cerevel, Click Therapeutics, Karuna/BMS, Lundbeck, Merck, Newron, Novartis, Otsuka, Sumitomo, Teva, and Terran. Grant Support: Lundbeck, Janssen, Otsuka, and Sunovion. Shareholder interests: Cerevel (public/stock), HealthRhythms (private/stock options), Karuna/BMS (public), LB Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (private/stock options), North Shore Therapeutics (private/stock), and Vanguard Research Group (private/40% owner). All other authors report no competing interests.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous