Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives of mitochondrial dysfunction of macrophages in periodontitis
- PMID: 40861497
- PMCID: PMC12375668
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1634909
Mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives of mitochondrial dysfunction of macrophages in periodontitis
Abstract
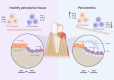
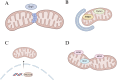
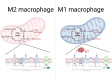
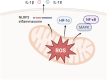
Periodontitis is a global inflammatory oral disease, and plaque-induced host excessive immune response is recognized as a major cause of its pathogenesis. In recent years, the relevance of mitochondrial dysfunction to periodontitis has been increasingly investigated, particularly with respect to macrophages, the key immune cells in the periodontal immune microenvironment. Mitochondrial dysfunction drives macrophage M1 polarization and osteoclast differentiation through mechanisms such as metabolic reprogramming, reactive oxygen species release, abnormal mitophagy, abnormal mitochondrial biogenesis and damaged mitochondrial dynamic. In addition, mitochondrial transfer in the periodontitis setting has been reported in several researches. In this review, we highlight the impact of mitochondrial dysfunction on macrophages in the periodontitis setting and summarize emerging therapeutic strategies for targeting mitochondria in periodontitis, including antioxidants, modulators of metabolic reprogramming, nanomaterials and photodynamic therapy.
Keywords: macrophage polarization; mitochondrial dysfunction; osteoclast differentiation; periodontitis mechanism; periodontitis treatment.
Copyright © 2025 Jia, Li, Huang, Wang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer HH declared a shared affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

