Laminin-derived peptide drives the cardiomyogenic potential and cardiac cells functionality
- PMID: 40861864
- PMCID: PMC12370699
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1629412
Laminin-derived peptide drives the cardiomyogenic potential and cardiac cells functionality
Abstract
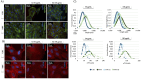
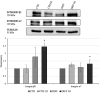
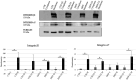
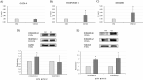
Laminin represents a major component of the basement membrane in cardiac tissue. Through integrins binding, laminin can sustain cell adhesion, proliferation, differentiation and mechanotransduction. The role of a small bioactive peptide (KKGSYNNIVVHV) derived from laminin in cardiac differentiation and functionality has been demonstrated. Briefly, results showed how the presence of laminin-derived peptide enhanced the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into cardiomyocytes-like phenotype, by modulating not only the cytoskeletal apparatus but also enhancing the cardiac and adhesion markers. Moreover, neonatal mouse cardiomyocytes in presence of the peptide showed well organized cytoskeletal rearrangements and regulated contractility. Therefore, in this study the role of laminin-derived peptide in guiding cardiomyogenesis has been characterized, opening innovative approaches in functional cardiac tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Keywords: bioactive peptides; cardiac tissue engineering; cardiomyogenesis; integrins; laminin.
Copyright © 2025 Casarella, Ferla, Di Francesco, Pagani, Di Varsavia, Regano and Boccafoschi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

