Preliminary evidence of CAR T-cell therapy activity in vitreoretinal lymphomas: An LOC network study
- PMID: 40862223
- PMCID: PMC12375968
- DOI: 10.1002/hem3.70208
Preliminary evidence of CAR T-cell therapy activity in vitreoretinal lymphomas: An LOC network study
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
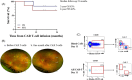
Figures
References
-
- Lam M, Touitou V, Choquet S, et al. Intravenous high‐dose methotrexate based systemic therapy in the treatment of isolated primary vitreoretinal lymphoma: an LOC network study. Am J Hematol. 2021;96(7):823‐833. - PubMed
-
- Younan N, Soussain C, Choquet S, et al. Isolated intraocular relapses of primary cerebral lymphomas: an LOC network study. Hematol Oncol. 2022;40(5):976‐986. - PubMed
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45‐56. - PubMed
-
- Choquet S, Soussain C, Azar N, et al. CAR T‐cell therapy induces a high rate of prolonged remission in relapsed primary CNS lymphoma: real‐life results of the LOC network. Am J Hematol. 2024;99(7):1240‐1249. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
