Hepatoprotective effect of lotus leaf against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via alteration of AMPK/SIRT1 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 40862425
- PMCID: PMC12377701
- DOI: 10.1590/acb407025
Hepatoprotective effect of lotus leaf against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats via alteration of AMPK/SIRT1 and Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
Abstract
Purpose: In this study, we scrutinized the protective effect of lotus leaf (LF) against high-fat diet (HFD) induced liver injury in rats.
Methods: The rats received the HFD for the induction of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Rats received the oral administration of LF (25, 50, and 100 mg/kg, b.w.). The insulin level, organ index, glucose level, hepatic, oxidative stress, lipid and cytokines parameters were measured. The different mRNA expression and histopathology were performed in the hepatic tissue.
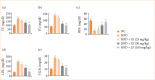
Results: LF treatment suppressed the insulin, glucose and HOMA-IR along with organ index (liver index and spleen index). LF treatment altered the level of liver parameters (aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, alkaline phosphatase, gamma-glutamyl transferase) and oxidative stress parameters in the serum, as well as the liver tissue. LF treatment altered the level of lipid parameters and fat parameters (total fat, perirenal fat, abdominal fat, epididymal fat); cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, interleukin-10, interleukin-17, interleukin-33); HO-1, and Nrf2. LF treatment altered the mRNA expression of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, interleukin-10, caspase-3, caspase-9, cytochrome C, cytochrome D, AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), FRX-1, liver X Receptor alpha, fibronectin, matrix metalloproteinase-9, inducible nitric oxide synthase, and transforming growth factor-β 1 (TGF-β1). LF treatment suppressed the necrosis of hepatocytes with less inflammatory cell infiltration in the liver tissue along with alteration of liver injury score.
Conclusion: The result showed the protective effect of LF against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via activating the AMPK/SIRT1 and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




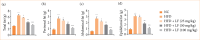

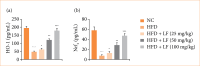

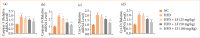



Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Paederia foetida on paracetamol-induced hepatobiliary disease in rats via alteration of inflammatory and Nrf2/HO-1 pathway.Acta Cir Bras. 2025 Aug 8;40:e409925. doi: 10.1590/acb409925. eCollection 2025. Acta Cir Bras. 2025. PMID: 40802356 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting fibrosis and steatosis: Nebivolol multi-pathway modulator ameliorates experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in rats through AMPK/mTOR and TGF-β1/α-SMA pathways.Bioorg Chem. 2025 Aug;163:108755. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2025.108755. Epub 2025 Jul 16. Bioorg Chem. 2025. PMID: 40682968
-
[Effect of Wenpi Pills on lipid metabolism in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease induced by various diets].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025 May;50(10):2730-2739. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20250120.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40686142 Chinese.
-
A systematic review of p53 regulation of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle.Redox Rep. 2018 Dec;23(1):100-117. doi: 10.1080/13510002.2017.1416773. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Redox Rep. 2018. PMID: 29298131 Free PMC article.
-
Statins for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Dec 27;2013(12):CD008623. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008623.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. PMID: 24374462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alsafty SAM, Abd El Motteleb DM, Sekinah AM, EL-sayed YM. Protective effect of dapagliflozin against non-alcoholic fatty liver in rats AMPK/SIRT1 pathway activation. Zagazig Univ Med J. 2024;30(9):4391–4404. doi: 10.21608/zumj.2024.306374.3487. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

