Skin-Inspired Healthcare Electronics
- PMID: 40862904
- PMCID: PMC12383305
- DOI: 10.3390/biomimetics10080531
Skin-Inspired Healthcare Electronics
Abstract
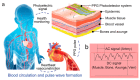
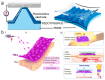
With the improvement in living standards and the aging of the population, the development of thin, light, and unobtrusive electronic skin devices is accelerating. These electronic devices combine the convenience of wearable electronics with the comfort of a skin-like fit. They are used to acquire multimodal physiological signal data from the wearer and real-time transmission of signals for vital signs monitoring, health dynamics warning, and disease prevention. These capabilities impose unique requirements on material selection, signal transmission, and data processing for such electronic devices. Firstly, this review provides a systematic introduction to nanomaterials, conductive hydrogels, and liquid metals, which are currently used in human health monitoring. Then, it introduces the solution to the contradiction between wireless data transmission and flexible electronic skin devices. Then, the latest data processing progress is briefly described. Finally, the latest research advances in electronic skin devices based on medical scenarios are presented, and their current development, challenges faced, and future opportunities in the field of vital signs monitoring are discussed.
Keywords: electronic skin; flexibility; health monitoring; vital signs monitoring; wearable devices.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors Fei Wang and Cai Chen were employed by the Guangzhou Shiyuan Electronic Technology Company Limited. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Prescription of Controlled Substances: Benefits and Risks.2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 6. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 30726003 Free Books & Documents.
-
Healthcare workers' informal uses of mobile phones and other mobile devices to support their work: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024 Aug 27;8(8):CD015705. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD015705.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 39189465 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advancements in Wearable Hydration-Monitoring Technologies: Scoping Review of Sensors, Trends, and Future Directions.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025 Jun 13;13:e60569. doi: 10.2196/60569. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2025. PMID: 40513095 Free PMC article.
-
Electrophoresis.2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jul 14. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36251838 Free Books & Documents.
-
Recent Advances in Conductive Hydrogels for Electronic Skin and Healthcare Monitoring.Biosensors (Basel). 2025 Jul 18;15(7):463. doi: 10.3390/bios15070463. Biosensors (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40710112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McDuff D. Camera Measurement of Physiological Vital Signs. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023;55:176. doi: 10.1145/3558518. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

