Cyber-Creativity: A Decalogue of Research Challenges
- PMID: 40863200
- PMCID: PMC12387658
- DOI: 10.3390/jintelligence13080103
Cyber-Creativity: A Decalogue of Research Challenges
Abstract
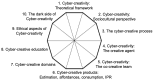
Creativity is the primary driver of our cultural evolution. The astonishing potential of artificial intelligence (AI) and its possible application in the creative process poses an urgent and dramatic challenge for humanity; how can we maximize the benefits of AI while minimizing the associated risks? In this article, we identify all forms of human-AI collaboration in this realm as cyber-creativity. We introduce the following two forward-looking scenarios: a utopian vision for cyber-creativity, in which AI serves to enhance and not replace human creativity, and a dystopian view associated with the pre-emption of all human creative agency caused by the rise of AI. In our view, the scientific community is called to bring its contribution, however small, to help humanity make steps towards the utopian scenario, while avoiding the dystopian one. Here, we present a decalogue of research challenges identified for this purpose, touching upon the following dimensions: (1) the theoretical framework for cyber-creativity; (2) sociocultural perspectives; (3) the cyber-creative process; (4) the creative agent; (5) the co-creative team; (6) cyber-creative products; (7) cyber-creative domains; (8) cyber-creative education; (9) ethical aspects; and (10) the dark side of cyber-creativity. For each dimension, a brief review of the state-of-the-art is provided, followed by the identification of a main research challenge, then specified into a list of research questions. Whereas there is no claim that this decalogue of research challenges represents an exhaustive classification, which would be an impossible objective, it still should serve as a valid starting point for future (but urgent) research endeavors, with the ambition to provide a significant contribution to the understanding, development, and alignment of AI to human values the realm of creativity.
Keywords: AI; artificial intelligence; creative process; creativity; cyber-creativity; education; ethics; sociocultural creativity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ali Sajid, Abuhmed Tamer, El-Sappagh Shaker, Muhammad Khan, Alonso-Moral Jose M., Confalonieri Roberto, Guidotti Riccardo, Ser Javier Del, Díaz-Rodríguez Natalia, Herrera Francisco. Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): What we know and what is left to attain trustworthy artificial intelligence. Information Fusion. 2023;99:101805. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.101805. - DOI
-
- Anantrasirichai Nantheera, Bull David. Artificial intelligence in the creative industries: A review. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2022;55:589–656. doi: 10.1007/s10462-021-10039-7. - DOI
-
- Bakker Michiel, Chadwick Martin, Sheahan Hannah, Tessler Michael, Campbell-Gillingham Lucy, Balaguer Jan, McAleese Nat, Glaese Amelia, Aslanides John, Botvinick Matthew M., et al. Fine-tuning language models to find agreement among humans with diverse preferences. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. 2022;35:38176–89.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources