The Role of Casein Phosphopeptide-Amorphous Calcium Phosphate (CPP-ACP) in White Spot Lesion Remineralization-A Systematic Review
- PMID: 40863292
- PMCID: PMC12387145
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb16080272
The Role of Casein Phosphopeptide-Amorphous Calcium Phosphate (CPP-ACP) in White Spot Lesion Remineralization-A Systematic Review
Abstract
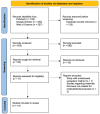
Amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) is a well-established bioceramic material known to promote the remineralization of dental hard tissues. White spot lesions (WSLs) represent the initial stage of enamel demineralization and are frequently observed in patients with fixed orthodontic appliances or inadequate oral hygiene. Although recommendations for remineralizing agents include both the prevention of lesion progression and the stimulation of tissue remineralization, the clinical efficacy of ACP-based materials remains under debate. This systematic review, registered in the PROSPERO database (CRD42024540595), aims to evaluate the clinical efficacy of casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP)-based products in the remineralization of WSLs and to compare these outcomes with those achieved using non-bioceramic approaches. Inclusion criteria comprised randomized clinical trials, prospective cohort studies, and pilot studies conducted on human subjects with WSLs affecting permanent teeth. Studies involving artificial WSLs or non-cariogenic enamel lesions were excluded. The quality of the included studies was assessed using the Cochrane Risk of Bias 2 (RoB 2) tool. Fourteen articles met the inclusion criteria and were analyzed. The main findings indicate that CPP-ACP is clinically effective in promoting the remineralization of WSLs, although the results were inconsistent across studies. Comparisons with placebo and resin infiltration treatments revealed greater efficacy for CPP-ACP. The combination of CPP-ACP with fluoride appeared to further enhance the remineralizing effect on WSLs. Additional standardized clinical studies with longer follow-up periods are warranted to confirm these outcomes.
Keywords: amorphous calcium phosphate; bioceramic material; casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate; enamel; remineralization; white spot lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Imani M., Safaei M., Afnaniesfandabad A., Moradpoor H., Sadeghi M., Golshah A., Sharifi R., Mozaffari H. Efficacy of CPP-ACP and CPP-ACPF for Prevention and Remineralization of White Spot Lesions in Orthodontic Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Acta Inform. Medica. 2019;27:199. doi: 10.5455/aim.2019.27.199-204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hussain U., Wahab A., Kamran M.A., Alnazeh A.A., Almoammar S., Alshahrani S.S.M., Niazi F.H., Alam S., Arif N., Campobasso A., et al. Prevalence, Incidence and Risk Factors of White Spot Lesions Associated With Orthodontic Treatment—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2024;28:379–399. doi: 10.1111/ocr.12888. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous