Artificial Intelligence-Guided Neuromodulation in Heart Failure with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Future Directions
- PMID: 40863380
- PMCID: PMC12386544
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd12080314
Artificial Intelligence-Guided Neuromodulation in Heart Failure with Preserved and Reduced Ejection Fraction: Mechanisms, Evidence, and Future Directions
Abstract
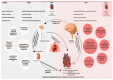
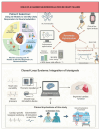
Heart failure, a significant global health burden, is divided into heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), characterized by systolic dysfunction and diastolic stiffness, respectively. While HFrEF benefits from pharmacological and device-based therapies, HFpEF lacks effective treatments, with both conditions leading to high rehospitalization rates and reduced quality of life, especially in older adults with comorbidities. This review explores the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in advancing autonomic neuromodulation for heart failure management. AI enhances patient selection, optimizes stimulation strategies, and enables adaptive, closed-loop systems. In HFrEF, vagus nerve stimulation and baroreflex activation therapy improve functional status and biomarkers, while AI-driven models adjust stimulation dynamically based on physiological feedback. In HFpEF, AI aids in deep phenotyping to identify responsive subgroups for neuromodulatory interventions. Clinical tools support remote monitoring, risk assessment, and symptom detection. However, challenges like data integration, ethical oversight, and clinical adoption limit real-world application. Algorithm transparency, bias minimization, and equitable access are critical for success. Interdisciplinary collaboration and ethical innovation are essential to develop personalized, data-driven, patient-centered heart failure treatment strategies through AI-guided neuromodulation.
Keywords: HFpEF; HFrEF; artificial intelligence; baroreflex activation therapy; cardiovascular technology; closed-loop systems; heart failure; neuromodulation; personalized medicine; remote health monitoring; vagus nerve stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Seferović P.M., Vardas P., Jankowska E.A., Maggioni A.P., Timmis A., Milinković I., Polovina M., Gale C.P., Lund L.H., Lopatin Y. The Heart Failure Association Atlas: Heart Failure Epidemiology and Management Statistics 2019. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021;23:906–914. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2143. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cheng R.K., Cox M., Neely M.L., Heidenreich P.A., Bhatt D.L., Eapen Z.J., Hernandez A.F., Butler J., Yancy C.W., Fonarow G.C. Outcomes in patients with heart failure with preserved borderline reduced ejection fraction in the Medicare population. Am. Heart J. 2014;168:721–730. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2014.07.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources