Exploring Heavy Metals Exposure in Urban Green Zones of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece): Risks to Soil and People's Health
- PMID: 40863908
- PMCID: PMC12390073
- DOI: 10.3390/toxics13080632
Exploring Heavy Metals Exposure in Urban Green Zones of Thessaloniki (Northern Greece): Risks to Soil and People's Health
Abstract
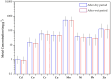
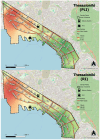
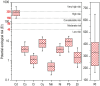
This study investigates the heavy metal contamination in urban and peri-urban soils of Thessaloniki, Greece, over a two-year period (2023-2024). A total of 208 composite soil samples were systematically collected from 52 sites representing diverse land uses, including high-traffic roadsides, industrial zones, residential neighborhoods, parks, and mixed-use areas, with sampling conducted both after the wet (winter) and dry (summer) seasons. Soil physicochemical properties (pH, electrical conductivity, texture, organic matter, and calcium carbonate content) were analyzed alongside the concentrations of heavy metals such as Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn. A pollution assessment employed the Geoaccumulation Index (Igeo), Contamination Factor (Cf), Pollution Load Index (PLI), and Potential Ecological Risk Index (RI), revealing variable contamination levels across the city, with certain hotspots exhibiting a considerable to very high ecological risk. Multivariate statistical analyses (PCA and HCA) identified distinct anthropogenic and geogenic sources of heavy metals. Health risk assessments, based on USEPA models, evaluated non-carcinogenic and carcinogenic risks for both adults and children via ingestion and dermal contact pathways. The results indicate that while most sites present low to moderate health risks, specific locations, particularly near major transport and industrial areas, pose elevated risks, especially for children. The findings underscore the need for targeted monitoring and remediation strategies to mitigate the ecological and human health risks associated with urban soil pollution in Thessaloniki.
Keywords: contamination indices; health risk; heavy metals; source apportionment; urban soils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Awewomom J., Dzeble F., Takyi Y.D., Ashie W.B., Ettey E.N.Y.O., Afua P.E., Sackey L.N.A., Opoku F., Akoto O. Addressing global environmental pollution using environmental control techniques: A focus on environmental policy and preventive environmental management. Discov. Environ. 2024;2:8. doi: 10.1007/s44274-024-00033-5. - DOI
-
- Xu X., Zhong Y., Cai S., Lei L., Peng J. Does Air Pollution Aggravate Health Problems in Low-Income Countries? Verification from Countries Along the Belt and Road. Sustainability. 2025;17:1796. doi: 10.3390/su17051796. - DOI
-
- Meravi N., Singh P.K., Prajapati S.K. Seasonal variation of dust deposition on plant leaves and its impact on various photochemical yields of plants. Environ. Chall. 2021;4:100166. doi: 10.1016/j.envc.2021.100166. - DOI
-
- Dawam M., Gobara M., Oraby H., Zorainy M.Y., Nabil I.M. Advances in Membrane Technologies for Heavy Metal Removal from Polluted Water: A Comprehensive Review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2025;236:461. doi: 10.1007/s11270-025-08035-6. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

