Effectiveness of Kaolinite with and Without Polyaluminum Chloride (PAC) in Removing Toxic Alexandrium minutum
- PMID: 40864071
- PMCID: PMC12390390
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins17080395
Effectiveness of Kaolinite with and Without Polyaluminum Chloride (PAC) in Removing Toxic Alexandrium minutum
Abstract
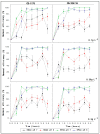
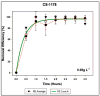
Alexandrium spp. blooms and paralytic shellfish poisoning pose serious economic threats to coastal communities and aquaculture. This study evaluated the removal efficiency of two Alexandrium minutum strains using natural kaolinite clay (KNAC) and kaolinite with polyaluminum chloride (KPAC) at three concentrations (0.1, 0.25, and 0.3 g L-1), two pH levels (7 and 8), and two cell densities (1.0 and 2.0 × 107 cells L-1) in seawater. PAC significantly enhanced removal, achieving up to 100% efficiency within two hours. Zeta potential analysis showed that PAC imparted positive surface charges to the clay, promoting electrostatic interactions with negatively charged algal cells and enhancing flocculation through Van der Waals attractions. In addition, the study conducted a cost estimate analysis and found that treating one hectare at 0.1 g L-1 would cost approximately USD 31.75. The low KPAC application rate also suggests minimal environmental impact on benthic habitats.
Keywords: Alexandrium spp.; cost estimate; harmful algal blooms; kaolinite; modified clays; removal rates; seawater; zeta potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Lewis A.M., Coates L.N., Turner A.D., Percy L., Lewis J., Mock T. A review of the global distribution of Alexandrium minutum (Dinophyceae) and comments on ecology and associated paralytic shellfish toxin profiles, with a focus on Northern Europe. J. Phycol. 2018;54:581–598. doi: 10.1111/jpy.12768. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hallegraeff G.M., Schweibold L., Jaffrezic E., Rhodes L., MacKenzie L., Hay B., Farrell H. Overview of Australian and New Zealand harmful algal species occurrences and their societal impacts in the period 1985 to 2018, including a compilation of historic records. Harmful Algae. 2021;102:101848. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2020.101848. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anderson D.M., Fensin E., Gobler C.J., Hoeglund A.E., Hubbard K.A., Kulis D.M., Landsberg J.H., Lefebvre K.A., Provoost P., Richlen M.L. Marine harmful algal blooms (HABs) in the United States: History, current status and future trends. Harmful Algae. 2021;102:101975. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.101975. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Manfrin C., De Moro G., Torboli V., Venier P., Pallavicini A., Gerdol M. Physiological and molecular responses of bivalves to toxic dinoflagellates. Invertebr. Surviv. J. 2012;9:184–199.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

