Gut-brain nexus: Mapping multimodal links to neurodegeneration at biobank scale
- PMID: 40864721
- PMCID: PMC12383272
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adu2937
Gut-brain nexus: Mapping multimodal links to neurodegeneration at biobank scale
Abstract
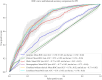
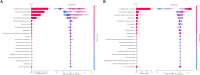
Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD) are influenced by genetic and environmental factors. We conducted a biobank-scale study to (i) identify endocrine, nutritional, metabolic, and digestive disorders with potential causal or temporal associations with AD/PD risk before diagnosis; (ii) assess plasma biomarkers' specificity for AD/PD in the context of co-occurring gut related traits and disorders; and (iii) integrate multimodal datasets to enhance AD/PD prediction. Our findings show that several disorders were associated with increased AD/PD risk before diagnosis, with variation in the strength and timing of associations across conditions. Polygenic risk scores reveal lower genetic predisposition for AD/PD in individuals with co-occurring disorders. Moreover, the proteomic profile of AD/PD cases was influenced by comorbid gut-brain axis disorders. Last, our multimodal prediction models outperform single-modality paradigms in disease classification. This endeavor illuminates the interplay between factors involved in the gut-brain axis and the development of AD/PD, opening avenues for therapeutic targeting and early diagnosis.
Figures


Update of
-
Gut-Brain Nexus: Mapping Multi-Modal Links to Neurodegeneration at Biobank Scale.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Nov 6:2024.09.12.24313490. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.12.24313490. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Aug 29;11(35):eadu2937. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adu2937. PMID: 39371139 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Lane C. A., Hardy J., Schott J. M., Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 25, 59–70 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Gustavsson A., Norton N., Fast T., Frölich L., Georges J., Holzapfel D., Kirabali T., Krolak-Salmon P., Rossini P. M., Ferretti M. T., Lanman L., Chadha A. S., van der Flier W. M., Global estimates on the number of persons across the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 658–670 (2023). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

