Human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) envelope structures in pre- and postfusion by cryo-EM
- PMID: 40864726
- PMCID: PMC12383274
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.ady8168
Human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) envelope structures in pre- and postfusion by cryo-EM
Abstract
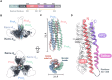
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs) are remnants of ancient infections that comprise ~8% of the human genome. The HERV-K envelope glycoprotein (Env) is aberrantly expressed in cancers, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases, and is targeted by patients' own antibodies. However, a lack of structural information has limited molecular and immunological studies of the roles of HERVs in disease. Here, we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of stabilized HERV-K Env in the prefusion conformation, revealing a distinct fold and architecture compared to HIV and simian immunodeficiency virus. We also generated and characterized a panel of monoclonal antibodies with subunit and conformational specificity, serving as valuable research tools. These antibodies enabled structure determination of the postfusion conformation of HERV-K Env, including its unique "tether" helix, and antibody-bound prefusion Env. Together, these results provide a structural framework that opens the door to mechanistic studies of HERV-K Env and tools for its evaluation as a potential therapeutic target.
Figures



References
-
- Flockerzi A., Ruggieri A., Frank O., Sauter M., Maldener E., Kopper B., Wullich B., Seifarth W., Müller-Lantzsch N., Leib-Mösch C., Meese E., Mayer J., Expression patterns of transcribed human endogenous retrovirus HERV-K(HML-2) loci in human tissues and the need for a HERV transcriptome project. BMC Genomics 9, 354 (2008). - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

