Linolenic Acid Inhibits Cancer Stemness and Induces Apoptosis by Regulating Nrf2 Expression in Gastric Cancer Cells
- PMID: 40864800
- PMCID: PMC12384521
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb47080646
Linolenic Acid Inhibits Cancer Stemness and Induces Apoptosis by Regulating Nrf2 Expression in Gastric Cancer Cells
Abstract
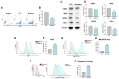
Although chemotherapy is the preferred treatment for gastric cancer, the therapeutic drugs currently available have limited efficacy and severe side effects. Cancer stem cells within tumor masses have the distinctive properties of self-renewal, maintenance, and resistance to chemotherapy. Hence, agents capable of targeting stemness in gastric tumors with minimal side effects are urgently required. Enzymes that generate reactive oxygen species contribute to the high oxidation levels observed in tumors. Additionally, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), an antioxidant transcription factor, regulates cancer stemness. Increasing evidence highlights the potential of nutritional supplementation to treat cancer stemness. ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids support human health and offer benefits for cancer treatment. Linolenic acid (LA), an ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, inhibits the expression of proteins associated with stemness and promotes apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. Our findings indicated that LA treatment substantially inhibited key characteristics of gastric cancer stemness and induced oxidative stress and caspase-3-mediated apoptosis by downregulating Nrf2-mediated expression. These results suggest that LA is a promising nutritional supplement for targeting cancer stemness in the treatment of gastric cancer.
Keywords: Nrf2; cancer stemness; gastric cancer; linolenic acid; ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- Marin J.J.G., Perez-Silva L., Macias R.I.R., Asensio M., Peleteiro-Vigil A., Sanchez-Martin A., Cives-Losada C., Sanchon-Sanchez P., Sanchez De Blas B., Herraez E., et al. Molecular Bases of Mechanisms Accounting for Drug Resistance in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2020;12:2116. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082116. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lee C.H., Tsai H.Y., Chen C.L., Chen J.L., Lu C.C., Fang Y.P., Wu D.C., Huang Y.B., Lin M.W. Isoliquiritigenin Inhibits Gastric Cancer Stemness, Modulates Tumor Microenvironment, and Suppresses Tumor Growth through Glucose-Regulated Protein 78 Down-regulation. Biomedicines. 2022;10:1350. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

