Differential gene expression drives muscle metabolic and structural differences in Liang Guang small spotted vs. large white pigs
- PMID: 40866463
- PMCID: PMC12391453
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17179-8
Differential gene expression drives muscle metabolic and structural differences in Liang Guang small spotted vs. large white pigs
Abstract
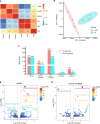
The Liang Guang Small Spotted (LGSS) pigs, an indigenous Chinese breed, are reported to exhibit desirable muscle attributes such as high intramuscular fat deposition, smaller muscle fiber diameter, and superior water-holding capacity. However, despite these merits, its commercial utility is constrained by suboptimal growth rates and diminished carcass yield. To explore transcriptomic differences potentially associated with distinct muscle phenotypes and identify targets for productivity enhancement, we performed integrated transcriptomic analysis of longissimus dorsi muscles (LDMs) from LGSS and Large White (LW) pigs. We characterized differentially expressed (DE) mRNAs, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), circular RNAs (circRNAs), and microRNAs (miRNAs), which were primarily enriched in key biological processes including glycolysis and carbon metabolism, structural organization, as well as signaling cascades such as HIF-1, AMPK, and PI3K-Akt. This study uncovers significant transcriptomic distinctions and identifies candidate regulatory molecules in LGSS pigs, offering potential biomarkers and a framework for future functional studies aimed at genetic improvement.
Keywords: Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs; Longissimus dorsi muscle; Pig; RNA sequencing; Whole-transcriptome sequencing.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Li, R. et al. Precise editing of myostatin signal peptide by CRISPR/Cas9 increases the muscle mass of Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs. Transgenic Res.29(1), 149–163 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Wei, Y. Y. et al. Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing in Guangdong small-ear spotted pig cells using an optimized electrotransfection method. Biotech. Lett.42(11), 2091–2109 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Peng, D. W. et al. Editing the cystine knot motif of MSTN enhances muscle development of Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs. Yi chuan = Hereditas43(3), 261–270 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Liu, X. et al. Disruption of the ZBED6 binding site in intron 3 of IGF2 by CRISPR/Cas9 leads to enhanced muscle development in Liang Guang Small Spotted pigs. Transgenic Res.28(1), 141–150 (2018). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

